Difference between revisions of "13. Glacial periods"
From SJS Wiki
Rbeniretto (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Return to [[History 8 Human Origins Concepts]] | Return to [[History 8 Human Origins Concepts]] | ||
| − | ''' | + | Glacial periods are periods in the Earth's history where the climate became ''cooler''. Interglacial periods are periods in Earths history where the climate became ''warmer''. The earth alternates between the two periods every 100,000 years. An example of a glacial period would be the last Ice Age. The last Ice age peaked around 16,000 BCE, and lowered temperatures around 65 degrees fahrenheit. Glacial and Interglacial periods change the organisms and ecosystems around them. For example, many large animals in North America became extinct due to the period changing to an interglacial period. |
| − | + | http://geology.utah.gov/wp-content/uploads/ice_ages2.gif | |
| + | -Will Leger | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Manual'' page 31 | |
| + | '''Sources''' | ||
| + | [http://arstechnica.com/science/2008/04/post-glacial-extinction/] | ||
| − | |||
| − | http:// | + | '''Pictures''' |
| − | + | [http://geology.utah.gov/wp-content/uploads/ice_ages2.gif] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 17 October 2015
Return to History 8 Human Origins Concepts
Glacial periods are periods in the Earth's history where the climate became cooler. Interglacial periods are periods in Earths history where the climate became warmer. The earth alternates between the two periods every 100,000 years. An example of a glacial period would be the last Ice Age. The last Ice age peaked around 16,000 BCE, and lowered temperatures around 65 degrees fahrenheit. Glacial and Interglacial periods change the organisms and ecosystems around them. For example, many large animals in North America became extinct due to the period changing to an interglacial period.
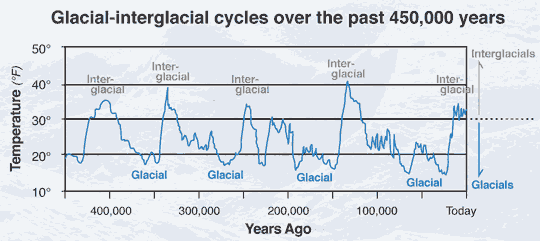
-Will Leger
Manual page 31
Sources [1]
Pictures
[2]