CERN Member pages
Contents
Use the space under your name to record your own work.
CERN Back to CERN mainpage
Melissa
Protons and neutrons are not fundamental because they are made up of things called quarks
Things that are fundamental cannot be broken down into smaller pieces
For every particle, there is a corresponding antiparticle or antimatter
When particles and antiparticles meet they annihilate into pure energy
Particles and antiparticles have opposite charges, the same mass, and are affected by gravity in the same way
Why is there so much more matter than antimatter in the universe?
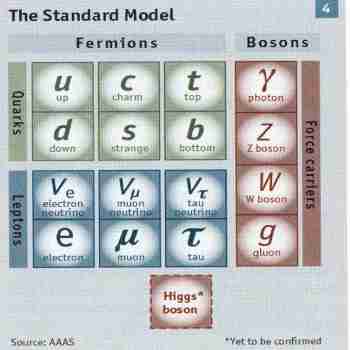
There are 6 types of quarks: Up, down, charm, strange, top, bottom
Quarks have fractional electrical charge
Hadrons - composite particles of quarks : Baryons, any hadron made of three quarks; Mesons, contain one quark and one antiquark
Leptons - 6 types, 3 with a charge (electron, muon, tau), 3 without a charge (neutrino)
Muon and tau decay rapidly so are not normally found
Three electron families - each charged particle and another neutrino
Brenden
1st Generation 4 Elementary Particles: up quark, down quark, electron, and neutrino.
Electrons and neutrinos are called leptons.
For every particle there is an Anti-Particle.
Emily
From the particle adventure website:
The Standard Model rises out of thousands of years of scientific inquiry, but most of the experiments that have given rise to our current conception of particle physics have occurred relatively recently.
In 1909, the prevailing theory of the atom's structure was that atoms were mushy, semi- permeable balls, with bits of charge strewn around them. This theory worked just fine for most experiments about the physical world.
BUT THEN Rutherford challenged this theory: shot up a stream of alpha particles at gold foil, allowing physicists to "look into" tiny particles they couldn't see with microscopes for the first time. These particles were expected to pass through the foil, but some of the alpha particles were deflected at large angles to the foil; some even hit the screen in front of the foil
Because some alpha particles were substantially deflected, Rutherford concluded that there must be something inside an atom for the alpha particles to bounce off of that is small, dense, and positively charged: the nucleus!!!!!!!!
Rutherford set the tone for further physics experiments, now they all have
-A beam (in this case, the alpha particles)
-A target (the gold atoms in the foil)
-A detector (the zinc sulfide screen)
Amanda
Particles
- wave functions with a probability of position in a given instant of time. (never know exactly where an electron is)
The Nucleus
- protons: positive electric charge (equal to absolute value of electron charge)
- neutrons: neutral electric charge, same mass as proton.
Quarks
- make up protons and neutrons
Two Kinds of Quarks
- Up quark
- charge of +2/3
- charge of +2/3
- Down quark
- charge of -1/3
- charge of -1/3
- Proton
- 2 Up quark, 1 Down quark
- 2 Up quark, 1 Down quark
- Neutron
- 2 Down quark, 1 Up quark
- 2 Down quark, 1 Up quark
Hadrons
- composite particles that consist of quarks
- ex. Protons, neutrons
Neeraj
Neutral particles do not leave a track, can create charged particles, when split (e.g. positron + electron split into separate positron and electron.) Charged particles leave a track as they travel, the particles charge and momenta can be calculated from the track. Bubble chamber filled with protons Other particles put in Accelerated and collide with protons -> new particles
David
Low energy
velocity appears to be completely transferred in an elastic collision.
Medium energy
Particles collide, the originally stationary particle goes upward while the originally moving particle travels downward, 2 small blue particles are also emitted directly in the direction of the original motion.
High energy
everything is the same as the medium energy collision except the blue particles are now larger and red.
All particles produced in collisions add up to the same charge. This law is known as the conservation of charge