Difference between revisions of "Earth Science 7 Africa 4"
| (37 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Earth Science 7- Regions]] | ||
=='''Africa'''== | =='''Africa'''== | ||
| − | + | ||
'''Countries:''' | '''Countries:''' | ||
Algeria | Algeria | ||
| Line 354: | Line 355: | ||
Map of Africa's Geology | Map of Africa's Geology | ||
| − | http:// | + | http://www.uni-koeln.de/sfb389/e/e1/download/geologie/afrika_gesamt/geol_africa.gif |
| + | <ref>http://www.uni-koeln.de/sfb389/e/e1/e1_download_e.htm</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===''Minerals in Africa''=== | |
| − | + | http://exploringafrica.matrix.msu.edu/images/map10.jpg | |
| − | + | Many common minerals found in Africa includes gold, iron, copper, diamonds, uranium, magnesium, and cobalt. <ref>[http://exploringafrica.matrix.msu.edu/students/curriculum/m20/activity2.php]<ref/> | |
| − | < | + | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===''Plate Tectonics''=== | |
| + | her is a map | ||
| + | http://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/GeolColBk/SmCol/AfricanPlateSmCol.gif | ||
| + | <ref>http://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/GeolColBk/SmCol/AfricanPlateSmCol.gif<ref/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The African Plate surrounds Africa and the Arabian Plate borders it on the northeastern side. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===''Boundary Types"=== | ||
| + | here is a map | ||
| + | http://www.regentsearthscience.com/tsunami/plates.gif | ||
| + | <ref>http://www.regentsearthscience.com/tsunami/plates.gif<ref/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The southwest boundary of the African plate is on the divergent, mid ocean ridge. Most of the African plate boundaries are divergent but to the north is a convergent boundary heading north and to the south is a small section of a transform boundary with the African side sliding northeast against the Antarctic Plate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===''Margin Types"=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is a sort of active margin off of northeast Africa but besides that the rest of the margins are passive. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===''Volcanoes''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanic Seven Summits in Africa: http://www.skimountaineer.com/ROF/VolcanicSeven.html | ||
| + | List: Name: Height (ft) Height (m) Location: Type: | ||
| + | 1. Kilimanjaro (Kibo) 19340 ft 5895 m Tanzania Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 2. Mount Kenya 17058 ft 5199 m Kenya Dissected Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 3. Kilimanjaro (Mawenzi)16893 ft 5149 m Tanzania Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 4. Mount Meru 14978 ft 4565 m Tanzania Stratovolcano with caldera | ||
| + | 5. Karisimbi 14787 ft 4507 Congo / Rwanda Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 6. Mikeno 14557 ft 4437 m Congo | ||
| + | 7. Mount Elgon 14178 ft 4321 m Kenya / Uganda Eroded stratovolcano with caldera | ||
| + | 8. Muhavura 13540 ft 4127 m Uganda / Rwanda | ||
| + | 9. Mount Cameroon 13435 ft 4095 m Cameroon Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 10. Pico del Teide 12198 ft 3718 m Canary Islands (Spain) Stratovolcano | ||
| + | 11. Visoke 12175 ft 3711 m Congo / Rwanda | ||
| + | 12. Sabinyo 11923 ft 3634 m Congo/Uganda/Rwanda | ||
| + | 13. Gahinga 11398 ft 3474 m Uganda / Rwanda | ||
| + | 14. Nyiragongo 11385 ft 3470 m Congo | ||
| + | 15. Hanang 11217 ft 3419 m Tanzania | ||
| + | 16. Emi Koussi 11204 ft 3415 m Chad | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most African volcanoes result from hotspots and the rifting in East Africa.. The East African rift has made the continent's highest and lowest volcanoes, ranging from the monster-sized Kilimanjaro to vents in Ethiopia's Danakil Depression that lies deep below sea level. Two volcanoes in Democratic Republic of the Congo Virunga National Park, Nyamuragira and Nyiragongo, are the sources for two-fifths of Africa's historical eruptions. Africa has the most volcanic centers with pyroclastic cones and fissure vents ), many of which lie within the East African Rift. The most common type of volcano in Africa is the stratovolcano. Because of the East African Rift, many volcanoes in Africa are located in East Africa. http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Volcanoes/Africa/description_africa_volcanics.html' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Andesitic magma comes from stratovolcanoes (Tarsoo Voon in Chad). Basaltic magma can be found in shield volcanoes ( such as the Jebel umm Arafieb in Sudan). Rhyolitic magma is found in cinder cones, tuff cones , and pyroclastic cones (such as the Todra Volcanic Field in Niger:cinder cone). Andesitic magma comes from stratovolcanoes (Tarsoo Voon in Chad). http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/region.cfm?rnum=0205 | ||
| + | |||
| + | The African tectonic plate covers all of the continent of Africa. Major volcanic regions are the afar triangle, which is located at a triple junction in the north east, and the Great Rift Valley, which extends from Syria in the middle east to Mozambique in the south. The Cameroon line is a chain of volcanoes formed by rifting from Annobón, Bioko, Príncipe and São Tomé in the Atlantic Ocean, through Cameroon towards Lake Chad. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here are some volcanoes in the countries of Africa: | ||
| + | Volcanoes of Cameroon | ||
| + | Manengouba | ||
| + | Mt Cameroon | ||
| + | Ngaoundéré | ||
| + | Oku | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Chad | ||
| + | Tarso Tôh | ||
| + | Tarso Toussidé | ||
| + | Tarso Voon | ||
| + | Emi Koussi | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Democratic Republic of Congo | ||
| + | Nyiragongo | ||
| + | Nyamuragira | ||
| + | May-ya-moto | ||
| + | Tshibinda | ||
| + | Karisimbi | ||
| + | Visoke | ||
| + | Mugogo | ||
| + | Mikeno | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Uganda | ||
| + | Fort Portal | ||
| + | Kyatwa | ||
| + | Katwe-kikorongo | ||
| + | Bunyaruguru | ||
| + | Katunga | ||
| + | Muhavura | ||
| + | Bufumbira | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Libya | ||
| + | Haruj | ||
| + | Wau-en-Namus | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Tanzania | ||
| + | Ol Doinyo Lengai | ||
| + | Kilimanjaro | ||
| + | Meru | ||
| + | Igwisi Hills | ||
| + | SW Usangu Basin | ||
| + | Ngozi | ||
| + | Izumbwe-mpoli | ||
| + | Rungwe | ||
| + | Kieyo | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Kenya: | ||
| + | Northern Rift (Turkana) | ||
| + | |||
| + | North Island | ||
| + | Central Island | ||
| + | South Island | ||
| + | The Barrier | ||
| + | Namarunu | ||
| + | Emuruangogolak | ||
| + | Central Rift Valley | ||
| + | |||
| + | Silali | ||
| + | Paka | ||
| + | Korosi | ||
| + | Ol Kokwe (Baringo) | ||
| + | Bogoria | ||
| + | West of Rift Valley | ||
| + | |||
| + | Homa Mountain | ||
| + | Kisingiri | ||
| + | Mt Elgon | ||
| + | Nyamaji | ||
| + | Southern Rift (Kenya Dome) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Menengai | ||
| + | Elmenteita Badlands | ||
| + | Ol Doinyo Eburru | ||
| + | Olkaria | ||
| + | Longonot | ||
| + | Suswa | ||
| + | East of Rift Valley | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mount Kenya | ||
| + | Chyulu Hills | ||
| + | Nyambeni Hills | ||
| + | Mega Basalt (Dukana) | ||
| + | Marsabit | ||
| + | Segererua | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Ethiopia: | ||
| + | Erta Ale Range | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ale Bagu | ||
| + | Alu | ||
| + | Borale Ale | ||
| + | Dalaffilla | ||
| + | Dallol | ||
| + | Erta Ale | ||
| + | Gada Ale | ||
| + | Hayli Gubbi | ||
| + | Nabro Range | ||
| + | |||
| + | Asavyo | ||
| + | Mallahle | ||
| + | Sorkale | ||
| + | Tat Ali Range | ||
| + | |||
| + | Borawli | ||
| + | Mat Ala | ||
| + | Tat Ali | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | West Danokil | ||
| + | |||
| + | Afdera | ||
| + | Alayta | ||
| + | Borawli | ||
| + | Dabbahu | ||
| + | Dabbayra | ||
| + | Dama Ali | ||
| + | Groppo | ||
| + | Kurub | ||
| + | Ma Alalta | ||
| + | Manda Hararo | ||
| + | Manda-inakir | ||
| + | Northern Ethiopian Rift | ||
| + | |||
| + | Adwa | ||
| + | Amoissa | ||
| + | Asmara | ||
| + | Ayelu | ||
| + | Beru | ||
| + | Dofen | ||
| + | Fentale | ||
| + | Gabillema | ||
| + | Hertali | ||
| + | Kone | ||
| + | Liado Hayk | ||
| + | Unnamed | ||
| + | Yangudi | ||
| + | Southern Ethiopian Rift | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alutu | ||
| + | Badda | ||
| + | Bilate River | ||
| + | Bishoftu | ||
| + | Bora-bericcio | ||
| + | Boset-bericha | ||
| + | Butajiri-silti | ||
| + | Chiracha | ||
| + | Cilallo | ||
| + | Corbetti | ||
| + | East Zway | ||
| + | Gedamsa | ||
| + | Hobicha | ||
| + | Korath Range | ||
| + | Mega Basalt Field | ||
| + | Mousa Alli | ||
| + | Sodore | ||
| + | Tullu Moje | ||
| + | Shala | ||
| + | Tepi | ||
| + | Tosa Sucha | ||
| + | Unnamed | ||
| + | Unnamed | ||
| + | Unnamed | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Sao Tome and Principe | ||
| + | Sao Tome | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanoes of Nigeria | ||
| + | Biu Plateau | ||
| + | http://www.volcanolive.com/africa.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanic Eruptions: | ||
| + | 7550 BC ± 1000 years | ||
| + | Paka in Eastern Africa | ||
| + | 6050 BC ± 1000 years | ||
| + | Meidob Volc Field Northern Africa | ||
| + | 6050 BC (?) | ||
| + | Menengai Eastern Africa | ||
| + | 1861 | ||
| + | Largest known historical eruption in Africa: Dubbi volcano, Eritrea. | ||
| + | 1960 | ||
| + | Feb. 29, Agadir, Morocco: 10,000–12,000 dead as earthquake set off tidal wave and fire, destroying most of city. | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://geology.gsapubs.org/content/28/4/291.full, http://www.volcanodiscovery.com/erupting_volcanoes.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | Volcanic Arcs: | ||
| + | The South Aegean Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanic islands in the South Aegean Sea formed by plate tectonics as a consequence of the subduction of the African tectonic plate beneath the Eurasian plate. | ||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/South_Aegean_Volcanic_Arc | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==="Plates and Earthquakes"=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | All of Africa is located on the African plate which is moving North Easterly. | ||
| + | The African plate forms a divergent boundary with the North and South American plates, and divergent boundaries with the Indian, Arabian, and Australian plates. | ||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/African_Plate | ||
| + | |||
| + | Earthquakes and MAgnitudes | ||
| + | Morocco | ||
| + | Feb, 12 2007 Iberian Peninsula earthquake: 6.1 | ||
| + | Feb, 24 2001 Morocco Earthquake: 6.4 | ||
| + | Democratic Republic of the Congo | ||
| + | Oct. 24 2002 Kalehe Earthquake: 6.2 | ||
| + | Dec, 5 2005Lake Tanganyika Earthquake: 8.8 | ||
| + | Algeria | ||
| + | Oct. 10 1980 El Ansam Earthquake: 7.3 | ||
| + | May 21 2003 Boumerdes Earthquake: 6.8 | ||
| + | Egypt | ||
| + | Nov. 22 1995 Egypt Earthquake: 7.1 | ||
| + | Libya | ||
| + | July 21, 365 Crete Earthquake: 8.5+ | ||
| + | Malawi | ||
| + | March 21, 1989 Malawi Earthquake:6.6 | ||
| + | Dec 19, 2009 Karonga Earthquake: 6.0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Earthquakes_in_Africa | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===''References''=== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:20, 28 April 2012
Contents
Africa
Countries: Algeria Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Canary Islands Cape Verde Central African Republic Ceuta Chad Comoros Côte d'Ivoire Democratic Republic of the Congo Djibouti Egypt Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Ethiopia Gabon Gambia Ghana Guinea Guinea-Bissau Kenya Lesotho Liberia Libya Madagascar Madeira Malawi Mali Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Melilla Morocco Mozambique Namibia Niger Nigeria Republic of the Congo Réunion Rwanda Saint Helena São Tomé and Príncipe Senegal Seychelles Sierra Leone Somalia South Africa Sudan Swaziland Tanzania Togo Tunisia Uganda Western Sahara Zambia Zimbabwe [1]
Latitude Range and Longitude:
Range:38°N-34°S; 17°W-49°E [2]
Elevation Range:
Highest Spot: Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania (19,334 ft) Lowest Spot: Lake Assal, Djibouti (-509 ft) [3]
Large Bodies of Water:
Longest River: Nile River 4125 mi. Largest Lake: Victoria Lake 26,834 sq. mi [4]
Major Topographic Features:
Mountain Ranges: Atlas Mountains, Drakensburg Mountains Large Basins:The Lake Chad Basin, The Congo Basin, The Niger Basin,The Nile Basin, The Orange Basin,Zambezi Basin [5]
Bordering Oceans and Seas:
Red sea, Mediterranean sea,Arabian sea, Atlantic Ocean, Indian ocean [6]
Africa Climate
Climate Zone
The climate zone of the southern region of Africa is classified on the Köppen climate classification chart as BWh-Dry (arid and semiarid) climates, Am-Tropical Monsoon Climate, Cwa-Humid subtropical climate, BSh-Dry (arid and semiarid) climates, BWh-Dry (arid and semiarid) climates, Aw-Tropical wet and dry or savanna climate, CWb-Maritime Temperate climates or Oceanic climates, Csb-Dry-summer subtropical or Mediterranean climates, Cfb-Maritime Temperate climates or Oceanic climates, and BSk-Dry (arid and semiarid) climates.
There are many cities in Africa, so the average monthly precipiation, rainfall, and high/low temperatures may differ. Here are a few examples of the averages in a southern town called Cape Town.
Cape Town Monthly Temperatures; Maximum and minimum:
| Cape Town Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual | |
| Avg. Max Temperature in ºF | 77 | 78 | 76 | 72 | 67 | 64 | 62 | 63 | 65 | 69 | 72 | 75 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature in ºF | 63 | 63 | 60 | 56 | 52 | 48 | 47 | 48 | 51 | 54 | 58 | 61 | ||
Average Precipitation in Cape Town
| Cape Town Precipitation | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Precipitation (inches) | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 1.60 | 2.70 | 3.70 | 3.30 | 3.00 | 1.60 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.70 | |
Factors that affect the climate of Africa:
Latitude: Africa latitude of 29° 00' S The specific latitude of Africa suggests its position in Northern Hemisphere and its moderate proximity to the equator. Africa is located towards the southern point of the African Continent. This country is close to the equator, so the region near the equator is hotter because it receives more sunlight. The southern tip of Africa where South Africa is located is not as hot as the region near the equator because it is not receiving vertical, direct rays of sunlight. This is how the latitude affects the climate of Africa. Elevation also affects Africa. The higher up you go, the colder it gets, while the lower you are (like sea level) the warmer the temperature is. The high southern and eastern plateaus, rarely falling below 600 m (2000 ft), have a mean elevation of about 1000 m (3300 ft). The southern region of Africa is also high. Northern Africa is highly elevated, with many mountains like the Atlas Mountains. There are areas with high elevation, like the Lesotho Highlands, while places like the Limpopo Plain are low. The topography of Africa is filled with almost plain and flat high land while the coastal regions are thin. Plains like the Sahel region is one example. Africa has many climates. Some regions are tropical, while some regions are known to be some of the driest places in the world (like the Sahara Desert). The climatic condition of South Africa is mainly arid and dry. Regions that make contact with the ocean usually have temperate conditions and weather. The eastern coastline is dominated by sub tropic weather. The days are usually filled with sunlight and nights are cold.
Prevailing Winds
The prevailing winds are moist winds from the NE and dry winds from the SE causing a varied climate. [11]
Vegetation
There are more than 20,000 different plants located in Africa. The fynbos vegetation zone mainly consists of evergreen hard-leave plants with usually fine, needle-like leaves. The by far biggest part of Africa is grassland. the plant cover is dominated by different grasses, low shrubs and acacia trees, mainly camel-thorn and white-thorn.Towards the north-west the vegetation becomes - due to the low precipitation - sparse. [12]
Proximity of Water
Africa is bounded by the Atlantic ocean in the West, and the Indian Ocean in the East. [13]\
Ocean Currents
The water to the West of Africa spins in a counter-clockwise motion. While on the Eastern side in the Indian Ocean,the currents veer towards the Cape of Good Hope, but if you go out to far, they veer sharply towards Australia. [14]
Pressure Zones
Africa is bounded by two high pressure zones on the east and west sides and has the trade winds passing right through it.[15]
Recent News
October: high temp, over 112 degrees Fahrenheit
Geology
Mining
Africa produces more than 60 metal and mineral products and is a major producer of several of the world’s most important minerals and metals including Gold, PGE’s, Diamonds, Uranium, Manganese, Chromium, Nickel, Bauxite and Cobalt.
Antimony World Production (2009): 187 Mt Production by country: South Africa Major companies: Metorex Key uses: Flame retardants, semi conductors
Bauxite World Production (2009): 201 Mt Production by country: Guinea Major companies: CBG, Rio Tinto Alcan Key uses: Aluminium production
Chromite World Production (2009): 23 000 Mt Production by country: South Africa (9 600) Major companies: Samancor, Assmang Key uses: Stainless steel production, superalloys
Coal World Production (2008): 5845 Mt Production by country: South Africa (236 Mt) Major companies: Anglo Coal, BHP Billiton Key uses: Energy generation
Cobalt World Production (2009): 62 000 t Production by country: DRC (25 000 t), Zambia (2 500 t), Morocco (1 600 t) Major companies: Gecamines, Norilsk Nickel Key uses: Metal alloys
Copper World Production (2009): 15.8 Mt Production by country: Zambia (0.655 Mt) Major companies: ZCCM Key uses: Electrical applications, construction
Diamonds World Production (2008): 168.0 Mct Value US$ (2007): $ 13 billion Production by country: South Africa, Botswana Major companies: De Beers Key uses: Jewellery, abrasives
Gold World Production (2009): 2 350 t Production by country: South Africa (210 t), Ghana (85 t) Major companies: AngloGold, Newmont Key uses: Jewellery, Investments
Iron ore World Production (2009): 2 300 Mt Production by country: South Africa (53 Mt), Mauritania (11 Mt) Major companies: Kumba Iron Ore, SNIM Key uses: Steel industry
Lead World Production (2009): 3.90 Mt Production by country: South Africa (0.05 Mt) Major companies: Rio Tinto Key uses: Motor vehicle batteries, chemical
Manganese World Production (2009): 9.60 Mt Production by country: South Africa (1.30 Mt), Gabon (0.81 Mt) Major companies: Samancor, Assmang Key uses: Ferroalloys
Molybdenum World Production (2009): 200 000 t Production by country: No production in 2009. Key uses: FerroAlloys
Nickel World Production (2009): 1 430 000 t Production by country: Botswana (36 000 t), South Africa (34 000 t) Major companies: Norilsk Nickel Key uses: Stainless steel, batteries, fuel cells
Palladium World Production (2009): 195 000 kg Production by country: South Africa (79 000 kg), Zimbabwe (4 800 kg) Major companies: Anglo Platinum, Impala Platinum and Wesizwe Key uses: Motor vehicle catalysts, electronic
Phosphates World Production (2009): 158 Mt Production by country: Morocco and Western Sahara (24 Mt), Tunisia (7 Mt), Egypt (3.3 Mt), South Africa (2.3 Mt), Togo (0.8 Mt), Senegal (0.7 Mt) Major companies: OCP Key uses: Fertiliser applications
Platinum World Production (2009): 178 000 kg Production by country: South Africa (140 000 kg), Zimbabwe (6 000 kg) Major companies: Anglo Platinum, Impala Platinum and Wesizwe Key uses: Motor vehicle catalysts, jewellery
Silver World Production (2009): 21 400 t Production by country: Minimal production in Africa Key uses: Electronics, photographic, jewellery
Tantalum World Production (2009): 1 160 t Production by country: DRC (100 t), Rwanda (100 t) Major companies: Mostly state owned Key uses: Electronic components; alloys
Tin World Production (2009): 307 000 t (Primary and Secondary sources) Production by country: DRC (12 000 t) Major companies: State owned Key uses: Packaging, alloys
Titanium World Production (2000): 5 720 Mt (Ilmenite and Rutile) Production by country: South Africa (1 100 Mt), Mozambique (206 Mt), Madagascar (60 Mt), Sierra Leone (60 Mt) Major companies: BHP Billiton, Anglo American, Exxaro Resources Key uses: Pigments and alloys
Tungsten World Production (2009): 58 000 t (concentrate) Production by country: No major production Key uses: FerroAlloys, filaments
Uranium World Production (2008): 43 853 tU Production by country: Namibia (4 366 tU), Niger (3 032 tU), South Africa (655 tU) Major companies: Areva Resources Key uses: Power generation, medical
Vanadium World Production (2009): 54.0 Mt (Vanadium pentoxide) Production by country: South Africa (19.0 Mt), Major companies: Highveld Steel and Vanadium Key uses: FerroAlloys
Zinc World Production (2009): 11 100 Mt Production by country: No major production Major companies: Rio Tinto Key uses: Galvanising, alloys
Zirconium World Production (2009): 1 230 Mt Production by country: South Africa (0.395 Mt), Major companies: Exxaro Key uses: Foundry applications, alloys[16]
Rocks
Map of Africa's Geology
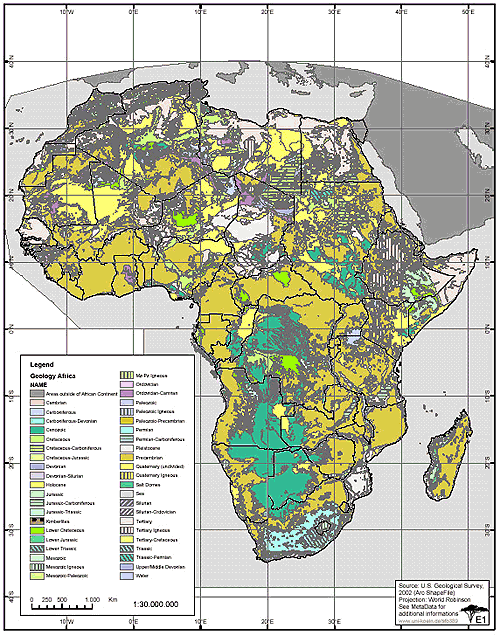 [17]
[17]
Minerals in Africa

Many common minerals found in Africa includes gold, iron, copper, diamonds, uranium, magnesium, and cobalt. Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found