16. Id effects of Babylonian Captivity
Return to History 8 Near East Vocabulary
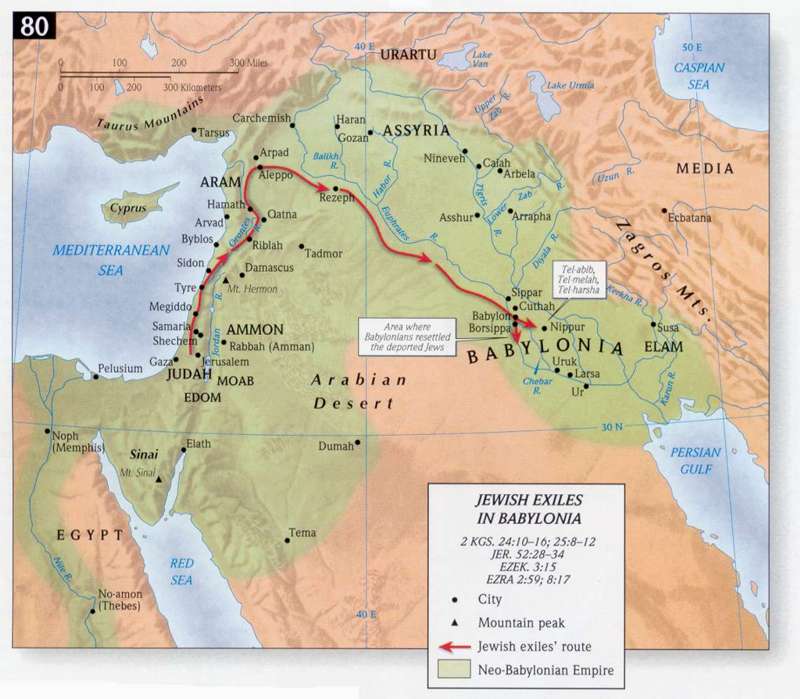
Originally, there were two kingdoms, Israel and Judah, that made up Israel. These kingdoms existed peacefully for almost 200 years. However, Assyria started meddling with the politics of this region in the southern Levant around 730 BC, trying to concentrate all power in the hands of the king, with whom the Assyrians negotiated directly. However, these two kingdoms neglected to pay tribute to the Assyrians, and resisted attempts to collect said tribute, so they were attacked by Assyria. Israel fell in 722 BC. but in Judah, Zedekiah, the king, revolted and allied himself with Egypt. But the city still fell, and Jerusalem was pillaged, the Temple destroyed. Nebuchadnezzar killed all of Zedekiah's sons and took him to Babylon, where over the next few years almost 5000 Jews were deported. This allowed Nebuchadnezzar to effectively control Judah by keeping all of its leaders in exile. While the Babylonian Jews were treated relatively well, this exile had a profound effect on the Jewish faith. Following the exile, the Jews did not return to worshiping idols, instead converting to polytheism. Additionally, the principal religious groups in Israel—the scribes, Pharisees, Sadducees, and others—originated during this time. They also changed their language, and when Cyrus the Great offered them the opportunity to return to Israel following two hundred years in exile, many of them did not wish to return.
Gabby Perkins
Sources:
Manual p.115-16
https://www.lds.org/manual/old-testament-student-manual-kings-malachi/enrichment-h?lang=eng