Asia earth science 5
Contents
- 1 Asia
- 2 China
- 2.1 Longitude and Latitude Ranges
- 2.2 Location
- 2.3 Area
- 2.4 Population
- 2.5 Large Bodies of Water
- 2.6 Bordering Oceans
- 2.7 Major Topographic Features
- 2.8 Elevation Range
- 2.9 Average Monthly Temperature (Fahrenheit) & Rainfall
- 2.10 Climate Zone
- 2.11 Natural Resources
- 2.12 Energy
- 2.13 Natural hazards
- 2.14 Geology
- 2.15 Tectonic Plates
- 3 Japan
- 4 Russia
- 5 Earth Science 7 Region
- 6 Citations
Asia
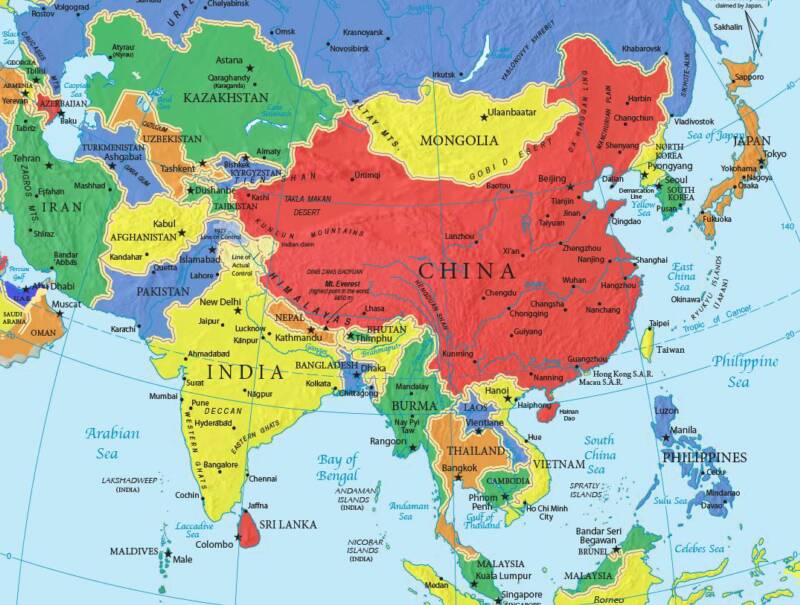 image 1
image 1
Countries of Asia
Afghanistan/ Armenia/ Azerbaijan /Bahrain/ Bangladesh/ Bhutan/ Brunei/ Cambodia/ China/ Georgia/ India/ Indonesia/ Iran/ Iraq/ Israel/ Japan/ Jordan/ Kazakhstan/ Kuwait/ Kyrgyzstan/ Laos/ Lebanon/ Malaysia/ Maldives/ Mongolia/ Myanmar/ Nepal/ "North Korea"/ Oman/ Pakistan/ Philippines/ Qatar/ Russia/ "Saudi Arabia"/ Singapore/ "South Korea"/ "Sri Lanka"/ Syria/ Tajikistan/ Thailand/ Timor-Leste/ Turkey Turkmenistan/ "United Arab Emirates"/ Uzbekistan/ Vietnam/ Yemen/
China
 image 2
image 2
Longitude and Latitude Ranges
Latitude Range: 49 degrees N-- 19 degrees N Longitude Range: 74 degrees E-- 119 degrees E [2]
Location
Eastern Asia, bordering the East China Sea, Korea Bay, Yellow Sea, and South China Sea, between North Korea and Vietnam[3]
Border countries: Afghanistan 76 km, Bhutan 470 km, Burma 2,185 km, India 3,380 km, Kazakhstan 1,533 km, North Korea 1,416 km, Kyrgyzstan 858 km, Laos 423 km, Mongolia 4,677 km, Nepal 1,236 km, Pakistan 523 km, Russia (northeast) 3,605 km, Russia (northwest) 40 km, Tajikistan 414 km, Vietnam 1,281 km[4]
Regional borders: Hong Kong 30 km, Macau 0.34 km Coastline: 14,500 km[5]
Area
Total Land Area: 9,596,961 sq km
Water: 27,060 sq km[6]
Population
Population: 1,336,718,015 (July 2011 est.)[7]
Large Bodies of Water
Yangtze River-- 3722 miles long Tonle Sap Lake-- 3860 sq. mi
Bordering Oceans
Pacific Ocean
Major Topographic Features
Qinghai-Tibet Plateau --4000 meters above sea level
Mt. Everest-- 8448 meters above sea level
Mongolia Plateau
Loess Plateau
Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau
Tarim Basin
Junggar Basin
Sichuan Basin
Northeast Plain
North China Plain
Yangtze Plain
Himalaya Mountain Range [8]
Elevation Range
8448 meters above sea level--- 154 meters below sea level [9]
Average Monthly Temperature (Fahrenheit) & Rainfall
Highs: Lows: Rainfall(inches): Jan. :34 15 0.1 Feb. :39 19 0.2 Mar. :52 30 0.4 Apr. :67 45 1.0 May. :79 55 1.1 Jun. :86 64 2.8 Jul. :87 70 6.9 Aug. :85 68 7.2 Sep. :78 57 1.9 Oct. :66 45 1.7 Nov. :50 31 0.2 Dec. :37 19 0.1
Climate Zone
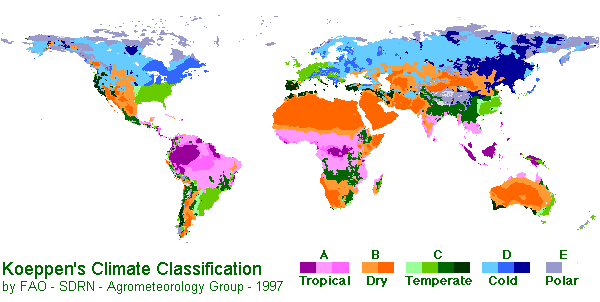 image 3
image 3
Climate: Köppen Climate Classification System
In A - Moist Tropical Climates are known for their high temperatures year round and for their large amount of year round rain.
B - Dry Climates are characterized by little rain and a huge daily temperature range. Two subgroups, S - semiarid or steppe, and W - arid or desert, are used with the B climates.
C - In Humid Middle Latitude Climates land/water differences play a large part. These climates have warm,dry summers and cool, wet winters.
D - Continental Climates can be found in the interior regions of large land masses. Total precipitation is not very high and seasonal temperatures vary widely.
E - Cold Climates describe this climate type perfectly. These climates are part of areas where permanent ice and tundra are always present. Only about four months of the year have above freezing temperatures.
Beijing, China is classified as Level C
The parts of China in the Himalayan Mountains are cold because it is at such a high elevation. The rest of China is at sea level so it is at an average temperture. The deep basins are also cooler because they provide shade.
China has the East China sea on its east side. Thus the East side gets more rain and therefore the temperture gets cooler.
Prevailing Winds: In North China, there is the South Westerlies and in the South there is the North Easterlies.[12]
Ocean Currents:In the Southeast China has the Kuroshio warm current. 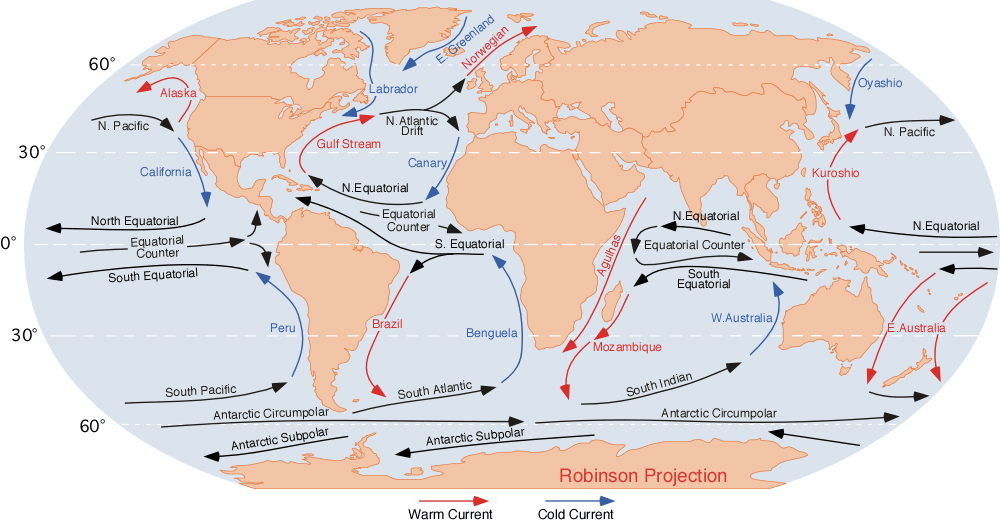 image 4
image 4
High Pressure Zone:
Low Pressure Zone:
Natural Resources
Coal, iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten, antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead, zinc, rare earth elements, uranium, hydropower potential (world's largest)[13]
Energy
Electricity - production: 3.446 trillion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - consumption: 3.438 trillion kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports: 17.39 billion kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports: 11.38 billion kWh (2009 est.) Oil - production: 4.273 million bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - consumption: 9.189 million bbl/day (2010 est.) Oil - exports: 480,600 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports: 4.753 million bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - proved reserves: 20.35 billion bbl (1 January 2011 est.)
Natural gas - production: 94.41 billion cu m (2010 est.)
Natural gas - consumption: 106.7 billion cu m (2010 est.)[14]
Natural hazards
Natural Hazards: Frequent typhoons (about five per year along southern and eastern coasts); damaging floods; tsunamis; earthquakes; droughts; land subsidence volcanism: China contains some historically active volcanoes including Changbaishan (also known as Baitoushan, Baegdu, or P'aektu-san), Hainan Dao, and Kunlun although most have been relatively inactive in recent centuries [15]
Geology
Mining
Petroleum (10 000 tons) 249097.9
Natural Gas (100 million cu.m) 25292.6
Coal (100 million tons) 3373.4
Iron (Ore, 100 million tons) 217.6
Manganese (Ore, 10 000 tons) 29658.5
Chromite (Ore, 10 000 tons) 537.1
Vanadium (Ore, 10 000 tons) 1304.9
Titanium (10 000 tons) 21385.0
Copper (Metal, 10 000 tons) 2929.0
Lead (Metal, 10 000 tons) 1314.7
Zinc (Metal, 10 000 tons) 4151.5
Bauxite (Ore, 10 000 tons) 72069.0
Nickel (Metal, 10 000 tons) 278.3
Tungsten (WO3, 10 000 tons) 291.6
Tin (Metal, 10 000 tons) 176.8
Molybdenum (Metal, 10 000 tons) 263.1
Antimony (Metal, 10 000 tons) 84.1
Gold (Metal, tons) 2075.1
Silver (Metal, tons) 37430.1
Rare Earths (REO, 10 000 tons) 2093.6
Magnesite Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 149660.4
Fluorspar Mineral (Mineral, 10 000 tons) 2835.0
Pyrite Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 194987.9
Phosphorus Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 389393.3
Potassium KCl (KCl, 10 000 tons) 27228.9
Sodium Salt NaCl (NaCl, 100 million tons) 1828.7
Mirabilite (Na2SO4, 100 million tons) 70.1
Barite Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 9839.0
Silicon Materials For Glass Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 124280.0
Graphite Mineral (Crystal) (Mineral, 10 000 tons) 5277.4
Talc Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 9387.0
Kaolin Ore (Ore, 10 000 tons) 55272.0 [16]
Rock Types
 image 7
image 7
Sedimentary Rocks form in China's rivers.(Yangtze River,Tonle Sap Lake)
Metamorphic rocks form near the Himalayan mountain range.
Igneous rocks form near china's volcano's.
Tectonic Plates
Image 12 
China sits mainly on top of the Eurasian Plate and a small portion of South West China sits on the Australian Plate.
Volcanoes [17]
Kunlun---------Kunlun volcano is a group of about 70 fresh-looking cinder cones in NW Tibet. Although the cones are not very large, thanks to its location in the Tibetan Plateau, Kunlun is the highest volcano in the northern hemisphere.
Tianshan-------Tianshan volcano is a group of cinder cones in the Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang Province in NW China. The Pechan cone was active in the 1st and 7th centuries AD.
Turfan---------Turfan volcano (allso referred to as the volcano of Ho-tscheu or Bischbalik) is an isolated volcanic cone near the city of Turfan in the Xinjiang Province of NW China.
Tengchong------Tengchong volcano is a volcanic field in southern China 40 km from the border with Burma (Myanmar) 430 km WNW of the city of Kunming.
Hainan Dao-----Hainan Dao volcano is a group of 58 cinder cones on the northern part of Hainan Island in SE China. Small fissure eruptions were recorded in 1883 from Lingao cone and in 1933 from Nansheling ridge.
Leizhou Bandao-Leizhou Bandao volcano is a volcanic field on the Leizhou peninsula 480 km SW of Hong Kong, across the Qiongzhou strait north of Hainan Dao Island. The field contains a group of Policene-Holocene cinder cones and the basaltic
Datong---------The Datong volcanoes are located 3 km northeast of Datong City at Xigelaoshan in North China west of Beijing. The volcanic field contains 30 cinder cones over an area of about 60 sq km.
Honggeertu-----Volcano is a volcanic field consisting of about 12 cinder cones located 335 km NW of Beijing in the Nei Mongul Province.
Arshan---------Arshan volcano is a newly discovered active volcanic field in the central Da Hinggan Mountains of Inner Mongolia in NE China, 70 km from the border with Mongolia. The field contains more than 40 cinder cones.
Keluo----------Keluo volcano is a volcanic field in NE China near the Russion border, south of the Heilongjiang (Black Dragon) River, 310 km NNW of the city of Daquiin. The volcanic group covers 350 sq km and contains 23 cones.
Wudalianchi----Wudalianchi volcano is one of the youngest volcanic fields on the mainland of Asia. It covers an area of about 500 sq km located at the junction between Xiaohinggan Mountains and Song-Nen depression in NE China.
Longgang-------Longgang volcano is a field of more than 150 cinder cones, lava flows and 8 maars located in Jilin Province of NE China, west of Changbaishan volcano. It covers an area of 1700 sq km.
Baitoushan-----Baitoushan volcano is a large stratovolcano at the NE China - N Korean border and is and the most active in China.
Jingbo---------Jingbo volcano (also known as Cingpo, Ching-pe, Chingpohu, or Jingbohu) is a young volcanic field in the Jingbo (or Jingpo) Lake area in NE China about 80 km SW of Mudanjiang city.
Earthquakes [18]
These earthquakes often occur near faults.
1290 09 27 - Chihli, China Fatalities 100,000
• 1556 01 23 - Shensi, China - M 8.0 Fatalities 830,000
• 1917 07 30 - Yunnan, China - M 7.5 Fatalities 1,800
• 1918 02 13 - Nan'ao, Guangdong, (Kwangtung), China - M 7.3 Fatalities 1,000
• 1920 12 16 - Haiyuan, Ningxia, China - M 7.8 Fatalities 200,000
• 1923 03 24 - Near Luhuo, Sichuan, China - M 7.3 Fatalities 3,500
• 1925 03 16 - Yunnan, China - M 7.1 Fatalities 5,800
• 1927 05 22 - Tsinghai, China - M 7.6 Fatalities 40,900
• 1931 08 10 - Xinjiang, China - M 8.0 Fatalities 10,000
• 1932 12 25 - Gansu, China - M 7.6 Fatalities 275
• 1933 08 25 - Sichuan, China - M 7.4 Fatalities 9,300
• 1948 05 25 - Sichuan, China - M 7.3 Fatalities 800
• 1950 08 15 - Assam - Tibet - M 8.6 Fatalities 1,526
• 1966 03 07 - Hebei, China - M 7.0 Fatalities 1,000
• 1966 03 22 - Hebei, China - M 6.9 Fatalities 1,000
• 1969 07 25 - Guangdong, China - M 5.9 Fatalities 3,000
• 1970 01 04 - Yunnan Province, China - M 7.5 Fatalities 10,000
• 1974 05 10 - China - M 6.8 Fatalities 20,000
• 1975 02 04 - Haicheng, China - M 7.0 Fatalities 2,000
• 1976 07 27 - Tangshan, China - M 7.5 Fatalities 242,769
• 2002 06 28 - Priamurye-Northeastern China border region - M 7.3
• 2002 12 25 - Kyrgyzstan-Xinjiang border region - M 5.7
• 2003 02 24 - Southern Xinjiang, China - M 6.3 Fatalities 261
• 2003 07 21 - Yunnan, China - M 6.0 Fatalities 16
• 2008 03 20 - Xinjiang-Xizang border region - M 7.2
• 2008 05 12 - Eastern Sichuan, China - M 7.9 Fatalities 87,587
• 2008 10 06 - Eastern Xizang - M 6.3 Fatalities 10
• 2009 07 09 - Yunnan, China - M 5.7 Fatalities 1
• 2010 04 13 - Southern Qinghai, China - M 6.9 Fatalities 2,968
Japan
==Longitude and Latitude Ranges== 35°N 139°E
==Longitude and Latitude Ranges== 35°N 139°E in Tokyo, Japan
The bodies of water that surround Japan are the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Philippine and East China seas to the south, and the Sea of Japan to the west.
The Japanese islands are the upper portions of vast mountains belonging to what is sometimes called the Circum-Pacific Ring of Fire. The Mountains cover about 75% of Japan. The Plains cover about 25% of Japan.
Average Monthly Temperature
Highs: January-52 degrees February-52 degrees March-54 degrees April- 68 degrees May-73 degrees June-75 degrees July-84 degrees August-87 degrees September-82 degrees October-70 degrees November-60 degrees December-54 degrees
Lows: January-35 degrees February-36 degrees March-38 degrees April-52 degrees May-58 degrees June-68 degrees July-71 degrees August-74 degrees September-69 degrees October-56 degrees November-48 degrees December-37 degrees
Climate Zone
Climate:
Prevailing Winds:
Ocean Currents:
High Pressure Zone:
Low Pressure Zone:
Mining
Japan was the world's largest producer and consumer of cadmium, the leading producer of selenium metal, electrolytic manganese dioxide, and titanium sponge metal; the second-leading producer of iodine, pig iron, nickel metal, and crude steel; the third-largest producer of copper metal, diatomite, and zinc metal; and the fourth-largest producer of cement. Japan also produced and had considerable resources of limestone, carbonate rocks (construction aggregates and dolomite), clays (bentonite and fire clay), pyrophyllite, and silica. Japan's mining industry has a steady decline right now. Japan is now relying heavily on imports for petroleum, iron ore, chromium, cobalt, copper concentrate (Japan was the world's largest importer), copper metal, primary aluminum, ilmenite, rutile, natural gas, gallium (Japan was the world's largest consumer), uranium, manganese (for all its requirements), indium (the world's largest consumer), nickel (world's largest consumer), and coal, although coal accounted for slightly more than half of all mineral production by value.
Tectonic Plates
[19] Click for picture
Rock Types
Japan is a mostly volcanic island located on an active plate rim. It belongs to the fire belt, a chain of volcanic activity around the Pacific Plate. Japan is a country with a very steep relief, a mountain range in the sea. The mountains are formed by the collision of two plates. This results in stress in the rock, tectonic movements, earth quakes and volcanism.
The mountains are composed of all types of rocks. Numerous volcanoes produced huge amounts of igneous rocks. All kinds of sedimentary rocks, sandstones, cherts and limestones, deposited on the floor of the Pacific Ocean, where aggregated by the convergent movement and uplifted by the orogeny. There are also reef limestones, formed along the coast of Japan and later uplifted.
[20] Click for picture
Russia
Longitude and Latitude Ranges
The latitude of Russia is 41°13′14″N to 81°50′35″N The longitude of Russia is 19°38'E to 169°01′W
Large Bodies of Water
The largest body of water in Asian Russia is Lake Baikal (31,494 km²). Two more large bodies of water in Russia is the Black Sea and the Gulf of Finland. The last two big bodies of water in Russia are the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk.
Bordering Ocean
Russia is one of the few countries in the world that have three oceans bordering it. One of which is the freezing cold Arctic Ocean. Another ocean is Atlantic ocean. The last ocean is the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Ocean is the biggest ocean in the entire world.
Major Topographic Features
Most of the major rivers in Russia flow from north to south. The rivers also become wider and deeper the further you progress east. They are also prone to heavy flooding during the spring thaw and autumn wet seasons. The Berezina River, flows for 380 miles (610km). It rises in Belarus and flows generally south past Borisov and Bobruysk into the Dneper River. It is navigable for most of its length. The Bug River flows for 480 miles (770km), rising in the Volhynian-Podolian hills in the western Ukraine. It flows north along the Polish-Ukrainian and Polish-Belarussian borders past Brest and then northwest through Poland to join the Vistula River near Warsaw. It is linked with the Dnepr by the Dnepr-Bug Canal via the Pina River and with the Niemen by the Augustov Canal via the Narva River. The Bug is also known as the Western Bug.The Daugava or Western Dvina is a river rising in the Valdai Hills flowing through Russia and Belarus, to drain into the Gulf of Riga, an arm of the Baltic Sea at Riga in Latvia. The total length of the river is 633 miles (1020km). It is connected by canal with the Berezina and Dnepr rivers. The Dnepr River flows for 1,430 miles (2,300km) through Belarus and the Ukraine. One of the longest rivers in Europe, it rises in the Valdai Hills, west of Moscow. It flows south through Belarus past Smolensk and Mogilev. It then travels through the Ukraine, past Kiev, Cherkasy, Kremenchug, Dneprpetrovsk, Zaporizhya, Nikopol, and Kherson into the Black Sea. Between Kremenchug and Nikopol the Dneper makes a big bend to the east. Since the construction in 1932 of the Dniprohes dam the Dnepr is navigable for virtually its entire course. Its tributaries include the Berezina, the Pripyat, and the Inhulets from the west and the Sozh, the Desna, the Orel, and the Samara from the east. The Dnepr is linked by canal with the Western Bug. The river Dniester, flows for 840 miles (1,352 km). It rises in the Ukraine, near the border with Poland, and flows toward the Black Sea. For a short while it marks the border of the Ukraine. It leaves this region and then flows through the Ukraine to the Black Sea. The Dniester, which rises in the Carpathians, within the territory of Galicia, becomes navigable at Sambor, and receives on the right the Stryj, the Swica, the Lomnica and the Bystrzyca, and on the left the Lipa, the Strypa, the Sereth and the Zbrucz. The Don is one of the major rivers of Russia. It rises near Tula, southeast of Moscow, and flows for a distance of about 1,220 miles (1,950km) to the Sea of Azov. From its source, the river first flows southeast to Voronezh, then southwest to its mouth. The main city on the river is Rostov on Don, its main tributary the Donets. At its easternmost point, the Don comes near the Volga. The two rivers are connected by the Volga-Don Canal whose length is 65 miles (105km). The Donets River rises in the Central Russian Upland, flowing south and then east through Russia and Ukraine for some 650 miles (1,050km). It rises northeast of Belgorod, which it then passes and flows generally southeast along the northern Donets Basin industrial region to join the Don River below Konstantinovsk. The Kuban River in southwestern Russia flows for 563 miles (906km) in length. It rises from glaciers on Mount Elbrus in the Greater Caucasus and flows north through narrow gorges, with many rapids, to the Stavropol Upland, where it turns westward in a broad, marshy floodplain to enter the Sea of Azov. Much of its water is diverted for irrigation. The river is navigable for most of its length.
Average Monthly Temperature
Monthly averages °F | °C
January Avg Low: -8° Avg High: -5° Avg precip: 3.99 cm February Avg Low: -9° Avg High: -4° Avg precip: 3.25 cm March Avg Low: -5° Avg High: 2° Avg precip: 2.72 cm April Avg Low: 2° Avg High: 11° Avg precip: 2.42 cm May Avg Low: 8° Avg High: 18° Avg precip: 3.92 cm June Avg Low: 12° Avg High: 22° Avg precip: 5.93 cm July Avg Low: 14° Avg High: 24° Avg precip: 5.56 cm August Avg Low: 12° Avg High: 22° Avg precip: 5.64 cm September Avg Low: 8° Avg High: 15° Avg precip: 4.61 cm October Avg Low: 3° Avg High: 8° Avg precip: 4.99 cm November Avg Low: -3° Avg High: 0° Avg precip: 3.82 cm December Avg Low: -8° Avg High: -4° Avg precip: 3.57 cm
Climate Zone
CLIMATE: Russia is both cold and warm depending on the time of year and the location in Russia. There is a cold and dry part of Russia called Siberia. Near the Black Sea in Russia it is warm and tropical.
PREVAILING WINDS:
OCEAN CURRENTS: On the eastern side of Russia there is a warm water ocean current coming from the Gulf of Mexico making the land which is very cold heat up causing fog inward on the land.
HIGH PRESSURE ZONES: The high pressure zone is coming inland so it is not as cold.
LOW PRESSURE ZONE: Russia is a low pressure zone and the winds are coming from the arctic ocean so the wind is freezing cold.
Mining
With bountiful and diverse minerals, Russia, the world's largest country in land area, occupying 75% of the former Soviet Union, had a significant percentage of the world's mineral resources and produced 14% of the world's total mineral extraction. Mining was the country's leading industry in 2002, and Russia was the largest producer of palladium and nickel (20% of world output), and ranked second in the production of aluminum and platinum-group metals (PGMs), third in potash, sixth in gold, and seventh in mine copper. Russia also produced a large percentage of the CIS's bauxite, coal, cobalt, diamond, lead, mica, natural gas, oil, tin, zinc, and many other metals, industrial minerals, and mineral fuels. Enterprises considered part of the mineral and raw-material complex contributed 70% of the budget revenues derived from exports; petroleum, petroleum products, and natural gas were Russia's leading export commodities in 2002; metals and chemicals also were leading export commodities.
Rock Type
Lithology refers to hard and loose rocks and deposits of various stages of continental lithogenesis, which form the surface layer involved in active daily and annual thermo-hydrologic cycles. These rocks and deposits contribute matter to the turnover of bio geochemical processes and soil formation, and deliver substances transported by runoff.
The lithogenic basis has parent rocks which soils comes from. These rocks form a layer of the geological hard and/or loose rocks, which are underground.
Phenacite is a rare beryllium mineral which is a silicate rock. Crystals are said to be rare, found in Minas Gerais, Zimbabwe, Russia and Colorado. The color ranges from colorless and white to tinted pink, yellow and brown.It has been said that the phenacite from different countries does have different properties and unique energetic vibrations alongside the general metaphysical blueprint.It is regarded at this time as being the carrier of the Highest Vibration of any known crystal.

Earth Science 7 Region
Citations
http://www.indexmundi.com/china/elevation_extremes.html
http://lasauniversity.tripod.com/water.html
http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/travel/continents/asia/
http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0001763.html
http://itouchmap.com/latlong.html
http://www.china.org.cn/english/environment/222905.html
https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/countrytemplate_ch.html
http://www.worldclimate.com/cgi-bin/grid.pl?gr=N35E139
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_are_the_surrounding_bodies_of_water_in_Japan
http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Asia-and-Oceania/Japan-TOPOGRAPHY.html
http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/vacationplanner/vacationclimatology/monthly/JAXX0085
http://www.allcountries.org/china_statistics/1_12_major_mineral_basic_reserves.html
http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Asia-and-Oceania/Japan-MINING.html#b
http://www.showcaves.com/english/jp/Geology.html
http://www.volcanodiscovery.com/china.html
http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/world/historical_country.php#china