Earth Science 7-1 South America
Contents
Tectonic Plates
South America is mostly located in the South American Plate, but a little bit of the Northwestern tip is in the Caribbean Plate. The South American Plate has a convergent boundary on the West with the Nazca Plate, and its boundary on the south is not determined. On the East, there is a divergent boundary, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, with the African Plate. The Northwestern South American Plate forms a divergent boundary and convergent boundary with the southern part of the Caribbean Plate. The Northern part of the Caribbean Plate is a transform boundary with the North American Plate, and the western part of the plate's boundary is a convergent boundary with the Cocos Plate. [1]
Active Margins
- The West Coast of South America because it is along a subduction boundary.
- The northwestern and southwestern coasts of South America are also along subduction boundaries
Passive Margins
- The East Coast of South America, not along any plate boundary.
[[1]]
Earthquakes
Earthquakes mainly occur along the western side of South America. Much of the igneous rock in South America is andesitic. The lava comes from volcanoes, near the South American plate, formed by earthquake activity.
Recent Earthquakes
- Arequipa, Peru: magnitude 5.4
- Santiago, Chile: magnitude 4.6
- Arequipa, Peru: magnitude 4.8
- Santiago, Chile: magnitude 4.7
- Ica, Peru: magnitude 4.5
- Santiago, Chile: magnitude 5.1
- Santiago, Chile: magnitude 6.7
- Santiago, Chile: magnitude 6.5
- Trujillo, Peru: magnitude 4.5
There are many others listed at [[2]]
Significant Earthquakes
- Armenia, Colombia: magnitude 6.2
- Coast of central Peru: magnitude 8.0
- Chile, Bolivia, Peru, and Argentina: magnitude 7.7
- Coast of Chile: magnitude 8.8
[[3]]
Volcanoes
There is many volcanoes on the West of South America where the Nazca Plate is subducting the South American Plate.The volcanoes have mostly andesitic magma because of the subduction occurring, therefore most of the volcanoes are composite volcanoes. However, there are some cinder cones, or pyroclastic cones, in this area.
Recent Eruptions
- Copahue in Argentina and Chile and is ongoing.
- Lascar in Chile and occurred in 2007.
- Llaima in Chile which occurred in 2008.
- Ubinas in Peru which occurred in 2007.
- Nevado Del Huila in Colombia showed heavy signs of activity in 2007 and 2008.
- Villarrica in Chile which occurred in 2011 and before in the past.
Geology:
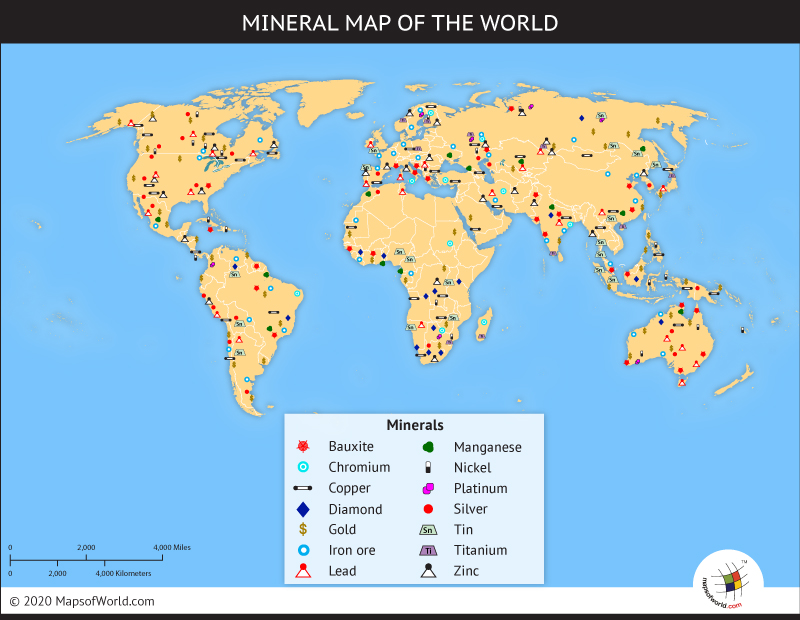
Mining and Mineral Resources:
- Peru- Peru has copper found inland.
- Chile- Silver is found in the northern tip. Copper is found both in the northern part and in the middle part. Gold is found also in the middle part. Coal is found in the southern part.
- Paraguay- There is oil in Paraguay.
- Bolivia- In Bolivia, there is silver and copper.
- Argentina- Oil is found all around in Argentina.
- Colombia- In Northern Colombia,there is oil to drill for.
- Venezuela- All over Venezuela, there is oil. In the middle of Venezuela, there is iron to mine.
- Guyana- Bauxite is found in the South-eastern part of Guyana.
- Suriname- In Suriname, there is Bauxite as well in the South-western part.
- Brazil- Bauxite is found inland. Diamond can be found in the Eastern part of Brazil. Iron is on the South-eastern part of Brazil. Lead and Zinc are found in the middle Western part of Brazil. Gold is found inland. Coal is found in the southern tip.
Minerals:
There are many minerals in South America. These minerals include copper, silver, gold, iron, bauxite, diamond, and lead and zinc. [5]
Mining Resources:
In South America, you can mine gold, silver, oil, and coal. [5]
Rock Types:
- Peru- The Western part, the area in which copper is found in Peru, is mostly composed of igneous and metamorphic rock because of the Andes Mountain Range. However, the Eastern side of Peru is mainly composed of sedimentary rock. There are also many rivers on the Eastern part of Peru causing the sedimentary rocks.
- Chile- The area in which silver is found in Chile, the Western Part, is mostly composed of igneous and metamorphic rock also because of the Andes Mountain Range. The areas in which copper are found are mostly composed of sedimentary rock because of river formations. The areas in which gold and coal are found are composed of mostly sedimentary rock also.
- Paraguay- The area in which oil is found in Paraguay is mostly composed of sedimentary rock. However, the south eastern side of Paraguay is mostly composed of igneous and metamorphic rock.
- Argentina- The one area in which oil is found is mostly composed of sedimentary rock because of the rivers, but the two other areas in which oil is found are mostly composed of metamorphic and igneous rock as a effect of the Andes Mountain Range. The majority of the country is composed of sedimentary rock.
- Brazil- The areas in which Bauxite, Lead, Zinc, Gold, Iron, and Diamonds are found are mostly composed of igneous and metamorphic rock because of the Guiana Range. The area in which Coal is found is composed primarily of sedimentary rock. This country is composed of primarily igneous and metamorphic rock.
- Bolivia- The area in which silver is found is composed primarily of sedimentary rock and flat terrain, but the area copper is found in is composed primarily of igneous and metamorphic rock and mountainous terrain.
- Colombia- The area in which oil is found is composed of sedimentary rock. This continent is composed primarily of sedimentary rock and flat terrain without mountain ranges.
- Ecuador- Equador is composed of sedimentary rock on the eastern and western sides of the country and flat terrain. There is also a strip igneous and metamorphic rock and mountainous terrain going down the center of the country.
- French Guiana- French Guiana is composed of primarily igneous and metamorphic rock with a slight sliver of sedimentary rock in the north eastern part of the country. French Guiana is mostly consisting of flat terrain with scattered mountains.
- Guyana- The area in which Bauxite is found in Guyana is composed mainly of igneous and metamorphic rock. In fact, the country is mostly made up of igneous and metamorphic rock. It consists of mostly rolling highlands creating the igneous and metamorphic rocks.
- Suriname- The area in which Bauxite is found is composed mainly of igneous and metamorphic rock because of a large area of mountainous terrain.
- Uruguay- There is a lot of igneous and metamorphic rock found in the central part of the country because of the large area of mountains. Around the metamorphic and igneous rock there is a lot of sedimentary rock.
- Venezuela- In two of the areas where oil is found the rock is mostly sedimentary, but in the two other areas the rocks are mostly igneous and metamorphic because of the mountainous area. Also in the area where iron is found, the rock is mostly igneous and metamorphic.
Climate Zone (use the Köppen Classification system)
- Af- Tropical rainforest. No dry season. The driest month has at least 2.40" (61 mm) of rain. Rainfall is generally evenly distributed throughout the year. All average monthly temperatures are greater than 64°F (18°C).
- Am- Tropical monsoonal. Pronounced wet season. Short dry season. There are one or more months with less than 2.40" (61 mm). All average monthly temperatures are greater than 64°F (18°C). Highest annual temperature occurs just prior to the rainy season.
- Aw- .Tropical savanna. Winter dry season. There are more than two months with less than 2.40" (61 mm). All average monthly temperatures are greater than 64°F (18°C).
- Cfc- Marine west coast. Mild with no dry season, cool summer. Average temperature of all months is lower than 72°F (22°C). There are one to three months with average temperatures over 50°F (10°C). Year around equally spread rainfall.
- Csc- dry summer season. cool summer.
- Cwc- dry winter season. cool summer.
Discussion
South America covers a lot of area. The Northern Part of South America is North of the Equator, so it has relatively warm temperatures. The Southern tip of South America is below 40 degrees South, which can cause the temperatures in the winter to drop. The Salinas Chicas, in Argentina, has an elevation of 40 m, one of the lower elevations in South America, while Aconcagua, also in Argentina, has an elevation of 6,960 m. The Salinas Chicas would be warmer than Aconcagua if they were at the same latitude. The air pressure would be higher at Aconcagua, because it has a higher elevation. The Andes mountain range would block out the clouds created over the Pacific Ocean, causing the areas to the east of the Andes to be like a desert. Areas on the coast of South America would have cooler temperatures due to the sea breeze. Areas on the coast of South America would also have clouds due to the evaporation and condensation of water from the ocean, possibly bringing rain. The trade winds at the equator come because the northern portion of South America has low pressure. The trade winds bring more winds in the winter than in the summer.Prevailing North easterlies bring winds to the Northeast areas of South America. Prevailing South Westerlies bring winds to the Southern tip of South America.East of the Andes, it is dry without much vegetation. Areas west of the Andes are lush and green, with a lot of vegetation. The Northern portion of South America is green because of the low pressure near the Equator, bringing rain. The top of South America, near the equator, has low pressure. At the middle of South America, 30 degrees latitude, there is high pressure. The South Pacific currents come up from the West. The Peru Current, a cold current, flows from south to north, and runs along the west coast of South America. The South Equatorial Current flows from east to west, going along the east coast of South America. The Brazil Current, a warm current, flows from north to south, and runs along much of the lower east coast of South America. Currents also climb up both sides towards the equator.
Countries-
Argentina:
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 34 00 S, 64 00 W
Elevation Range-
lowest point= Laguna del Carbon- 105 m.
highest point= Cerro Aconcagua- 6,960 m.
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Rio de la Plata
Rivers= Rio Parana
Major Topographic Features- Andes mountain range,Pampas low lands, Patagonian plateau
Bordering Oceans- South Atlantic Ocean
[8]
Bolivia:
Image of Bolivia- [4]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 17 00 S, 65 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest Point= Nevada Sajama- 6,542 m.
Lowest Point= Rio Paraguay- 90 m.
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Lago Titicaca
Rivers= Rio Mamore, Rio Beni, Rio Lauca
Major topographic features- Andes Mountains, Altiplano plateau, Amazon Basin lowland plains
Bordering Oceans- none
[8]
Brazil:
Image of Iguazu Falls in Brazil- [5]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 10 00 S, 55 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Pico da Neblina 2,994 m
Lowest point= Atlantic Ocean- 0 m.
Large bodies of water (including Rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= Rio Parana, Amazon
Major topographic features- none
Bordering Oceans- North Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean
[8]
Chile:
Image- [6]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 30 00 S, 71 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Nevada Ojos del Salado- 6,880 m.
Lowest point= Pacific Ocean- 0 m.
Large Bodies of Water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Strait of Magellan
Rivers= Rio Lauca
Major Topographic features- Andes mountains, Atacama Desert
Bordering Oceans- South Pacific Ocean
[8]
Colombia:
Image of St Andres - [7]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 4 00 N, 72 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Pico Cristobal Colon 5,775 m.
Lowest point= Pacific Ocean- 0 m.
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= Amazon
Major topographic features- Andes Mountains, Pico Cristóbal Colón Mountain
Bordering Oceans- North Pacific Ocean
[8]
Ecuador:
Image of Bata Ecuador- [8]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 2 00 S, 77 30 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Chimborazo- 6,267 m
Lowest point= Pacific Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= Rio Napo, Rio Putumayo
Major topographic features- Andes Mountains
Bordering Oceans- Pacific Oceans
[8]
Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas):
Image of Saunders Island- [9]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 51 45 S, 59 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Mount Usborne- 705 m
Lowest point= Atlantic Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= none
Major topographic features- rocky, hilly, mountainous with some boggy, undulating plains
Bordering Oceans- South Atlantic Ocean, Scotia Sea
[8]
French Guiana (France):
Image- [10]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges-
metropolitan France: 46 00 N, 2 00 E
French Guiana: 4 00 N, 53 00 W
Guadeloupe: 16 15 N, 61 35 W
Martinique: 14 40 N, 61 00 W
Mayotte: 12 50 S, 45 10 E
Reunion: 21 06 S, 55 36 E
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Mont Blanc- 4,807 m
Lowest point= Rhone River delta- -2 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= Rhône, Seine, Rhine
Major topographic features-
metropolitan France: mountainous part- Pyrenees in south, Alps in east; but mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in north and west
French Guiana: low-lying coastal plains rising to hills and small mountains
Guadeloupe: Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, and seven other islands, most of them are volcanic in origin
Martinique: mountainous with indented coastline; dormant volcano
Mayotte: generally undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks
Reunion: mostly rugged and mountainous; fertile lowlands along coast
Bordering Oceans- Mediterranean Sea, Bay of Biscay
[8]
Guyana:
Image- [11]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 5 00 N, 59 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Mount Roraima- 2,835 m
Lowest point= Atlantic Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= Courentyne, Koetari Rivier, Kutari, New, Essequibo, Takutu, Demerara, Berbice
Major topographic features- mostly rolling highlands; low coastal plain; savanna in south
Bordering Oceans- North Atlantic Ocean
[8]
Paraguay:
Image- [12]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 23 00 S, 58 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Junction of Rio Paraguay and Rio Parana 46 m
Lowest point= Cerro Pero 842 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Represa de Itaipu
Rivers= Rio Parana, Rio Paraguay
Major topographic features- Cerro Pero- highest mountain and point in Paraguay, Gran Chaco
Bordering Oceans- None
[8]
Peru:
Image Punta Sal Beach- [13]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 10 00 S, 76 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point=Nevado Huascaran- 6,768 m
Lowest point=Pacific Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Lago Titicaca
Rivers= Amazon, Rio Ucayali, Rio Madre de Dios, Rio Huallaga, Rio Marañón
Major topographic features- western coastal plain, Andes Mountains, eastern lowland jungle of Amazon Basin
Bordering Oceans- South Pacific Ocean
[8]
South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands:
Image- [14]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 54 30 S, 37 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Mount Paget (South Georgia)- 2,934 m
Lowest point= Atlantic Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= none
Rivers= none
Major topographic features- most of the islands rise steeply from the sea and are rugged and mountainous; South Georgia is largely barren and has steep, glacier-covered mountains; the South Sandwich Islands are of volcanic origin with some active volcanoes
Bordering Oceans- South Atlantic Ocean, Scotia Sea
[8]
Suriname:
Image-[15]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 4 00 N, 56 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Juliana Top- 1,230 m
Lowest point= unnamed location in the coastal plain- -2 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= W. J. van Blommestein Meer, Stondansie Projekt, Kabalebo Projekt
Rivers= Koetari Rivier, Tapanahoni Rivier, Lawa Rivier, Litani Rivier, Suriname Rivier, Marouini
Major topographic features- mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps
Bordering Oceans- North Atlantic Ocean
[8]
Uruguay:
Image- [16]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 33 00 S, 56 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Cerro Catedral- 514 m
Lowest point= Atlantic Ocean- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Embalse de Rincón del Bonete, Embalse de Paso de Palmar, Laguna Merín
Rivers= Uruguay, Rio Cuareim, Rio Negro
Major topographic features- mostly rolling plains and low hills; fertile coastal lowland
Bordering Oceans- South Atlantic Ocean
[8]
Venezuela:
Image- [17]
Latitude and Longitude Ranges- 8 00 N, 66 00 W
Elevation Range-
Highest point= Pico Bolivar- 5,007 m
Lowest point= Caribbean Sea- 0 m
Large bodies of water (including rivers)-
Large bodies of water= Lago de Valencia, Lago de Maracaibo
Rivers= Rio Orinoco
Major topographic features- Guiana Highlands, Pica Bolivar, Andes Mountains, Maracaibo Lowlands, Llanos central plains
Bordering Oceans- Caribbean Sea
[8]
References
- ↑ Earth Science,McDougal Littell Inc., 2005.
- ↑ List of Earthquakes. Info. ExchangeRate.com. Inc. http://listofearthquakes.com/earthquakes-south-america
- ↑ Historic World Earthquakes. Info. USGS. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/world/historical_country_mag.php#chile
- ↑ Google Earth. Map. Google Inc.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Maps of World. Picture. Map XL Inc. http://www.mapsofworld.com/world-mineral-map.htm
- ↑ Geology Maps. Picture. About.com. http://geology.about.com/od/othernationgeomaps/Geologic_Maps_of_Other_Countries.htm
- ↑ World. Picture. National Weather Service. http://www.worldclimate.com/cgi-bin/grid.pl?gr=N29W095
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 South America. Picture/Info. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/wfbExt/region_soa.html
--Jma 13:22, 14 October 2011 (CDT) Katie, Arisa, and Jacqueline