Earth Science 7-Africa2
Earth Science 7-Global Regions Index
Contents
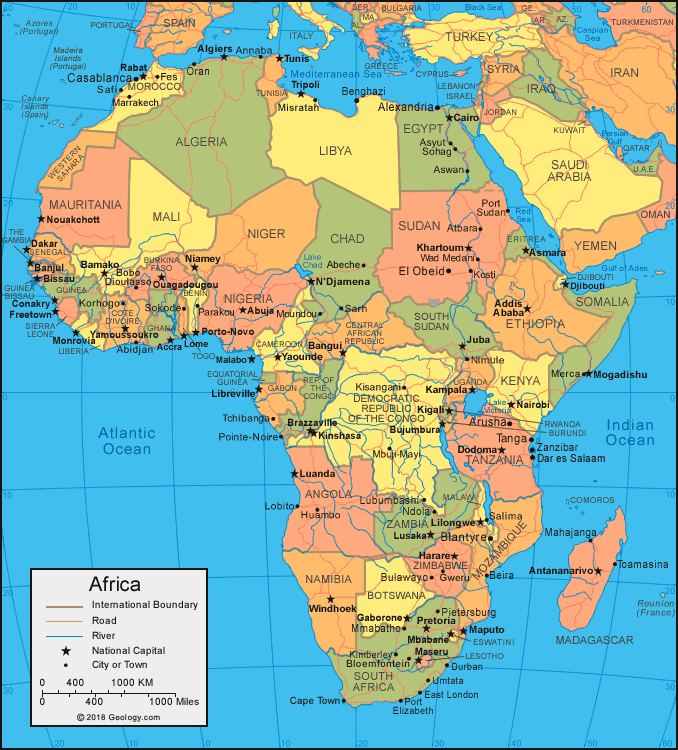
Countries
Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Republic of Congo, Democratic Republic of The Congo, Cote d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast (Cote d'Ivoire), Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe,
Latitude/Longitude
Latitude: 37°N - 37°S Longitude: 18°W - 53ºE
Elevation Range
Highest Point:
Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
5,895.1368 meters
Lowest Point: Lake Assal, Djibouti 156.0576 meters below sea level
Bodies of Water
Lakes: Chad, Nasser, Tanganyika, Victoria
Rivers: Blue Nile, Congo, Limpopo, Niger, Nile, Orange, Senegal, Volta, White Nile
Seas: Arabian, Mediterranean, Red, Baltic, Black
Topographic Features
Atlas Mountains, Nambi Desert, Great Rift Valley, Congo River Basin, Kalahari Desert, Ethiopian Highlands, Nubian Desert, Libyan Desert, Ahaggar Mountains, Sahara Desert, Qattara Depression, Jabel Toubkal, Ras Dejen, Emi Koussi, Adamwa Mountains, Cameroon Mountain, Bie Plateau, Namib Desert, Thabana Ntleyana, Margherita Peak, Mount Kenya, Bemaraha Plateau, Jos Plateau
Bordering Oceans
Atlantic Ocean and Indian Ocean
Mediterranean Sea
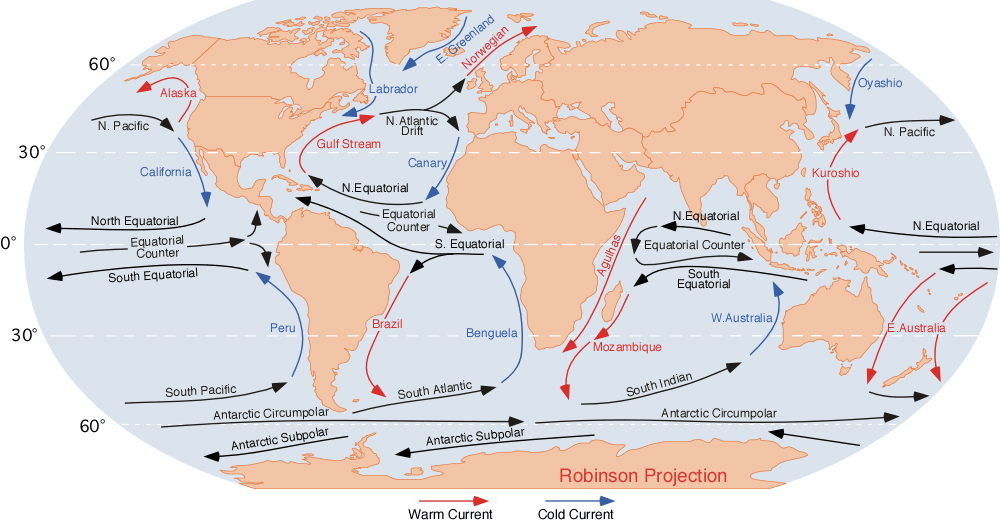
Currents
Eastern side of Africa has cold currents, while western side has warm currents
Ice Cover
very rarely does ice occur
Tides
Very low tides, and not a lot of waves.
Salinity
[4] Atlantic ocean- High salinity but lower towards equator. (34-37 ppt)
Indian Ocean- A little above average salintity (32-37 ppt)
Mediterranean- High salinity because of high evaporation.
Black Sea & Baltic Sea- Low salinity because large rivers flow into them.
Arabian Sea- High salinity because of high evaporation.
Wave Action
Coastal erosion is a problem for several countries in the western Indian Ocean, including Kenya, Tanzania and Mozambique. Tsunamis are not frequent, but they do occur
Climate Zones(Top to Bottom)
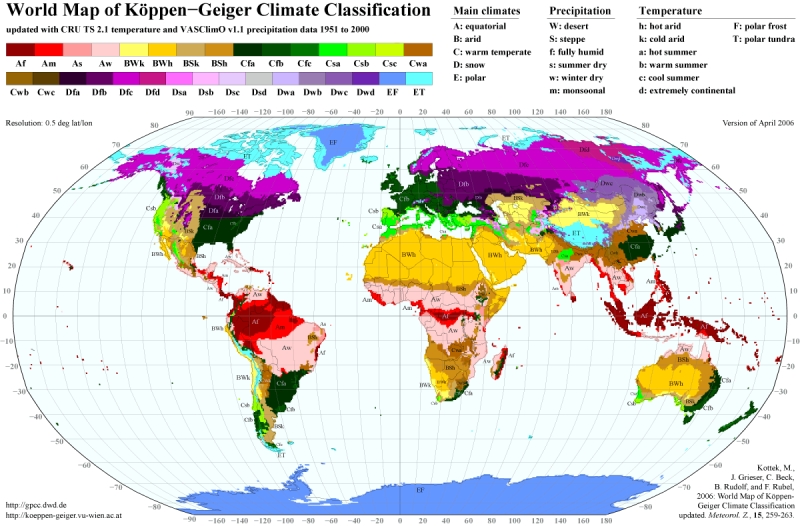
-Hot, dry summer, warm temperate- Northern coast line(fairly small)
-Hot arid steppe- The Sahara desert (very large)
-Cold arid steppe- The Sahel desert (thin strip under Sahara)
-Equatorial winter dry-
-Equatorial monsoonal-Surrounding Equator- Rainforest
-Equatorial fully humid- On the equator- Rainforest
-Equatorial monsoonal- Surrounding Equator- Rainforest
-Equatorial winter dry-
-Warm temperate, winter dry, warm summer-
-Hot arid steppe- Kalahari desert
-Hot arid desert- Kalahari desert
-Cold arid desert- Kalahari desert
-Warm temperate, warm summer, fully humid- Southern tip of Africa
Climate Controls
-The equator and the Prime Meridian pass through it causing hot temperatures
-The elevation reaches up to 1400 meters which is cooler than sea level
-Has many deserts which cause extreme climate changes daily and receive very little rain
-On the west coast, ocean currents are cooler, while on east coast, ocean currents are warmer
-Almost all of Africa has mild wind currents which make it hotter
-Mostly desert and jungle which means there are pretty extreme climate changes
Minerals
Coal- mostly in the southern half
Petroleum- Northern part and western coast
Iron ore- mainly southern tip; a few at the northern side
Manganese- Very few around coastal areas
Copper- Southern area
Tin- Above Bight of Benin
Uranium- Eastern side
Chromite- Eastern area
Cobalt- southern area
Phosphate rock- Northeastern edge of Africa
Diamonds- Mid-Southern area
Gold- Western areas
Most of the minerals in Africa are either on the Southern tip in the livestock area or along the all of the coasts in Africa
There is lots of phosphate rock near the Atlas Mountains
Tectonic Plates
On the African Plate- Divergent Boundary everywhere but the North and Northeastern sides, which are Convergent
-Volcanoes-
-Two chains of continental volcanoes- one on the Mideastern side, one on the middle of the west side
-mostly Cylinder Cone Volcanoes- Rhyolitic Magma
-Nyiragongo Volcano- currently erupting- Pyroclastic Volcano
-Ol Doinyo Lengai Volcano- currently erupting- Stratovolcano and Pyroclastic Volcano
-Erta Ale Volcano- Currently erupting- Shield Volcano
-Nabro Volcano- Caldera- erupted in 2011
-Earthquakes-
-almost all of the earthquakes occurred along the African Plate Boundary
recent earthquakes:
-4.6 in Kenya-10 km deep-occurred Tuesday, April 17th, 2012
-biggest earthquake in the last 20 years was a 7.4 along the African boundary line that was 14 miles deep (1990)
Geological Map
Sources
[1]-Countries in Africa
[2]- Elevation Range
http://www.koolasun.co.za/weather/sa-sea-conditions.html -Tides
Student Atlas of the World- Topographic Features
Google Earth: Water Bodies & Latitude/Longitude
[5]- Climate Zones
[4]- Salinity
[7]- Tectonic Plates
http://www.saeonmarine.co.za/SADCOFunStuff/TidesOfSA.htm -tides
Google Earth
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.africaguide.com/country.htm
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/af.htm
- ↑ 3.0 3.1

- ↑ 4.0 4.1 http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/285876/Indian-Ocean/22777/Surface-salinity
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/present.htm
- ↑ 6.0 6.1

- ↑ 7.0 7.1 http://www.volcanodiscovery.com/erupting_volcanoes.html
- ↑ 8.0 8.1