Earth Science 7-Central America2
Earth Science 7-Global Regions Index
[[1]]
Contents
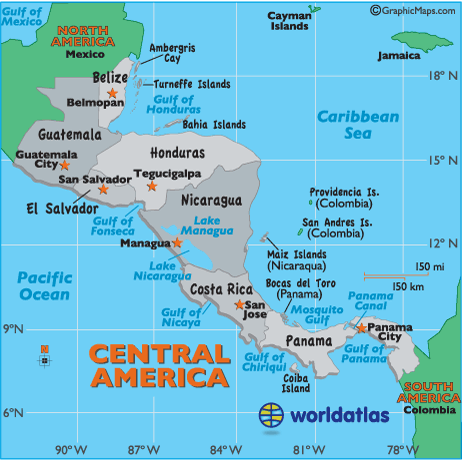
Countries in Central America
[[2]]
1. Belize (Capital, Belmopan)
2. Guatemala (Capital, Guatemala City)
3. Honduras (Capital, Tegucigalpa)
4. Nicaragua (Capital, Managua)
5. Costa Rica (Capital, San Jose)
6. Panama (Capital, Panama City)
7. El Salvador (Capital, San Salvador)
8. Cuba (Capital, La Havana)
9. Puerto Rico (Capital, San Juan)
10. The Lesser of Antilles
Islands in Central America
[[3]]
1. Turneffe Islands
2. Isla de la Bahia Islands (Bay Islands)
3. Providencia Islands
4. San Andres Islands
5. Maiz Islands
6. Coiba Island
7. Cayos Cocinos (Hog Islands)
8. Swan Islands
9. Ometepe Island
10. Pearl Islands
11. Taboga Islands
12. Cebaco Islands
13. Coiba Islands
14. Barbados
15. Haiti (Capital, Port-au-Prince)
16. Dominican Republic (Capital, Santo Domingo)
17. Jamaica
Main Bodies of Water in and Surrounding Central America
[[4]]
1. Gulf of Honduras
2. Caribbean Sea
3. Mosquito Gulf
4. Panama Canal
5. Gulf of Panama
6. Gulf of Chiriqul
7. Gulf of Nicaya
8. Pacific Ocean
9. Gulf of Fonseca
10. Lake Managua
11. Lake Nicaragua
12. Lake Izabal
13. Motagua River
Latitude and Longitude
General Knowledge
(17°-5°N) (91°-15°W)
Elevation Range
[[5]]
The highest point in Central America is the Tajamulco Volcano, which is located in the country of Guatemala. It is 13,845 feet (4,220 meters) above sea level.
The lowest point in Central America is the Carribean Sea, which is 0 feet (0 meters) above sea level.
Topographic Features
[[6]]
Sierra Madre de Chiapas (Volcano Range)
Cordillera Isabella (Volcano Range)
Cordillera de Talamanca (Volcano Range)
Rainforests
Barrier Reef
The Blue Hole (An opening to a former Ice Age cave and popular dive spot)
Sierra Madre Mountains
The Central Highlands
Carribean Lowlands
Central Mountains
Bocas del Torro (Collection of Islands)
San Blas Archipelagos (Collection of Islands)
Darian Gap (Jungle)
Climate Zones
The climate in Central America is equatorial monsoonal, and equatorial winter dry. Central America is surrounded by water on either side of it, some of the countries are islands so you can expect proximity to water to control and affect its weather. Central America is above sea level, keeping it cooler than if it was at sea level. There are many volcanoes and mountains that contribute to the climate change, by blocking strong winds or other precipitation. Central America is fairly close to the equator causing it to have a warm climate. Warm ocean currents (S. Equatorial) affect the eastern side of Central America, while the western side is affected by a cold California Current. Wind currents affect the western side of Central America with the North Equatorial Current, and the eastern side is affected by the Gulf Stream Current. The small islands affect the climate zones because they are tropical and their warm humid air moves into the mainland affecting the climate zones.
The Koepper Chart was very helpful with this study of the clinmate zones.
Major Natural Disasters
[[9]]
1. 1917 Earthquake in Guatemala with 600 fatalities.
2. 1976 Earthquake in Guatemala with 23,000 fatalities.
3. 1998 Hurricane Mitch and flooding throughout all of Central America with 12,000 fatalities.
4. 2001 Earthquake in El Salvador with 850 fatalities
5. 2004 Rains in Haiti and the Dominican Republic with 2,400 fatalities.
6. 2005 Flooding in Central America with 1,400 fatalities, 1,200 of these were in Guatemala.
7. 2005 Tropical Storm Stan and mudslides in Guatemala and El Salvador with at least 225 fatalities.
8. August 2008 Hurricane in Haiti with 500 fatalities.
9. 2009 7.1 Earthquake in Honduras with 6 fatalities and 40 injuries.
9. January 2010 Earthquake in Haiti with 230,000 fatalities.
10. 2010 Hurricane Agatha and local volcanic eruption in Guatemala with over 100 fatalities.
Ocean
Currents
Mcdougal Littell Earth Science Textbook
[[10]]

1.) Gulf Stream - The Gulf stream current is a warm current. Of all the warm currents, it has been studied most extensively. It begins in the Caribbean Sea and follows the east coast of North Carolina. On the Surgasso side it has a cold core ring and on the continent side it has a warm core ring.
2.) California - The California current is a cold current, due to its passage through northern latitudes, which cools it. Upwelling is responsible for the high productivity of California's nearshore waters, and phytoplankton thrives here. The upwelling period lasts from March until September, when northwesterly winds die down and the cold upwelling begins to sink.
Near Water
[[11]]
1.) Gulf of Tehuantepec- very feared, because winds at 30-40 mph go through it, and they can rapidly increase to gale, storm, and even hurricane force, bringing with it huge seas that can push you hundreds of miles out to sea
2.) Caribbean Ocean
3.) Pacific Ocean
Salinity of Water
The salinity is around 30 ppt. (3 O/oo) for Central America.
Ice Cover
It is doubtful that there is any ice in Central America due to it being so near to the equator.
Tides
Caribbean Coast - For a short period of time NNE swell, 8 seconds, has arrived pushing in,reaching 3 feet overhead.
Pacific Coast - SSW swell with sets 1-2 feet overhead and around 17 second period will fade, and leave chest to head high surf. Waist to chest SW swell for most of the coast with a 12 second period, with a few shoulder high sets from the WNW
Geology

Gold
In 2007, a Costa Rica gold mine was suspended because there was risk of pollution, from the Glencairn Gold Corporation
El Salvador is known to have gold.
[[12]]
Overall Mining Central America
If you go to: http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/2007/myb3-2007-bh-cs-es-ho-nu-pm.pdf you can find a fantastic chart that lists the production of mineral commodities from 2003-2007 for many different minerals. The chart is located on Section 6.6 and 6.7 of the document.
[[13]]
There isn't a lot of mining happening in Central America, because people aren't sure if it would be good for world economy. Central American's aren't so sure if it would be best for Central America.
Honduras [[14]]
Doesn't support mining, because it costs them money, and because of all the dangers involved with mining, however, many people have gone individually to mine, due to gold's increasing value.
Lead, silver, and zinc are mined at Breakwater Resources Ltd.'s El Mochito underground mine.
Some gold is mined at Goldcorp Inc.'s San Martín and Yamana Gold Inc.'s San Andrés open pit heap-leach mines.
In 2007, mainstream gold mining accounted for $75.4 million worth of exports.
Costa Rica
Shut down a gold mine in 2007 due to pollution risks.
Nicaragua [[15]]
Mining is not a large industry in Nicaragua, but the small pieces of gold and silver they can come up with goes to exportation taxes.
Nicaragua has deposits of gold and silver, as well as industrial mineral deposits of calcium, clay, gypsum, limestone, and pumicite.
Quaternary volcanic and felsic rocks can be found in the east of Nicaragua and a belt of Paleozoic metamorphic rocks is located in the north.
Cuba
Mines for nickel, and its the second most important exportation other than sugar
Belize [[16]]
Clay, limestone, marble, sand, and gravel is what Belize used to export, but not recently, and none of these were reported to have been exported in 2007.
Clay, dolomite, gravel, and sand were/are mined along the Belize, Monkey, and Sibun Rivers, and also along the North Stann and South Stann Creeks.
Very small amounts of gold have been uncovered, along with traces of barite and gypsum.
El Salvador
Has gold and other precious minerals, but they are having a hard time getting mining rights. Some mining advocates have been issued death threats or been murdered, and only a few mining companies have gained mining rights.
Panama [[17]]
Used to be the route for shipping precious minerals to other places, but does not produce most of them
Has two of the wealthiest undeveloped copper mines, with 1.4 billion tons of copper, but is not allowed to mine them, due to certain laws.
Used to have two gold mines in Santa Rosa and Remance, but they were shut down after a stock market scandal in Indonesia and Canada.
The mining company Petaquilla drew 500 ounces of gold per month until laws were created that restricted it.
Jamaica [[18]]
Exported gypsum, marble, silica sand, clay, normal sand, gravel, alumina, and soil.
Under the Minerals Law, all minerals are owned by the government.
Jamaican bauxite was used during the war.
Dominican Republic [[19]]
The Dominican Republic is opposed to mining, but there are still some mining companies.
The mine bauxite, and have 22 million dollars worth of bauxite.
Plate Tectonics
The plates surrounding Central America include, the Cocos Plate on the western coast, and on the eastern side, it is between the South and the North American plates.

Boundary Types
The Cocos Plate is a Transform Fault Line in the Mid-American Trench, and the South American Plate forms a divergent boundary with the North American Plate.
Margins
http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/geol212/converg_margins.htm
The Ring of Fire, in which Central America is located, is a convergent plate margin.
Volcanoes
http://www.geo.mtu.edu/volcanoes/santamaria/eruption.html
http://news.sky.com/home/world-news/article/15639807
There are many volcanoes located along the southwestern coast of Central America. There are not as many on the northeastern coast and there are also many Volcanoes in the Lesser of Antilles.
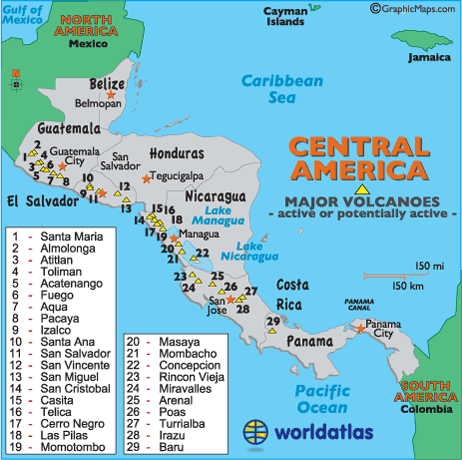
A few of the volcanoes include:
Santa Maria : In 1902, after being inactive for at least 500 years, the Santa Maria erupted on October 25, 1902. Following a series of Central American volcanoes, it killed at least 5000 people, and darkened the skies for days.
Atitlan
Almolonga
Toliman
Acatenango
Fuego
Aqua
Pacaya : In May, in 2005, a reporter was killed when this volcano erupted, and they got to close. Three children reported missing after Pacaya erupted. Around 1,600 people were evacuated from the volcano's slope. Between 2 and 3 inches of ash built up on the streets of the southern part of Guatemala City, which is 15 minutes from Pacayo, and this ash buildup resulted int eh closing of the La Aurora International Airport. In 1998, this volcano also erupted, forcing evacuations and the closing of the airport.
Izalco
Santa Ana
San Salvador
San Vincente
San Miguel
San Cristobal
Casita
Telica
Cerro Negro
Momotombo
Las Pilas
Masaya
Mombacho
Concepcion
Rincon Vieja
Miravelles
Arenal
Poas
Turrialba
Irazu
Baru
Earthquakes
http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqarchives/year/byyear.php
[Google Earth]
There are many earthquakes on the southwestern coast of Central America.
One earthquake in Central America was in Haiti onJanuary 12, 2010. It was a 7.0 on the Richter Scale and there were 316,000 fatalities.
References
[20] -- http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/camerica.htm
General knowledge
[21] -- http://geography.about.com/library/faq/blqzantilles.html
[22] -- Koeppen Geiger Map
[23] -- http://www.scaruffi.com/politics/disaster.html
[24] -- http://msnbc.msn.com/id/30976505/ns/world_news-americas/t/deadly-quake-strikes-central-america-coast/#.TspuAmNnGW4
McDougal Littell Earth Science Textbook
[25] -- http://ceres.ca.gov/ceres/calweb/coastal/waters.html
[26] -- http://www.svcalypso.com/2010/04/the-dreaded-gulf-of-tehuantepec/
[27] -- http://www.earthworksaction.org/media/detail/costa_rican_gold_mine_suspended_due_to_pollution_risks
[28] -- http://www.businesspanama.com/investing/opportunities/mining.php
[29] -- GEOLOGICAL MAP
[30] -- http://www.discoverjamaica.com/gleaner/discover/geography/mining.htm
[31] -- http://countrystudies.us/dominican-republic/50.htm
[32] -- http://www.oxfamamerica.org/press/pressreleases/central-american-mining-could-undermine-economic-well-being
[33] -- http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/2007/myb3-2007-bh-cs-es-ho-nu-pm.pdf
http://www.tulane.edu/~sanelson/geol212/converg_margins.htm
http://www.geo.mtu.edu/volcanoes/santamaria/eruption.html
http://news.sky.com/home/world-news/article/15639807
http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqarchives/year/byyear.php