Earth Science 7-Europe3
Earth Science 7-Global Regions Index
Contents
Countries
Europe has many countries. They are Albania, Andorra,Armenia,Azerbaijan,Belarus,Belgium,Bosnia & Herzegovina,Bulgaria,Croatia,Cyprus,Czech Republic,Denmark,Estonia,Finland,France,Georgia,Germany,Greece,Hungary, United Kingdom,and Vatican City (Holy See). Europe is the second smallest of the worlds continents. Europe is made up of 40 politically independent countries. The western part of Russia is included in Europe and a small portion of western Turkey is also included.
North Atlantic Drift Current
The North Atlantic Drift Current or NADC, is a slow-moving body of water located between about 50°-64°N and 10°-30°W. NADC is also considered to be an extension of the North Atlantic Current. It is recognized as a shallow, widespread and variable wind-driven surface movement of warm water that covers a large part of the eastern sub-polar North Atlantic and slowly spills into the Nordic Seas.The current is unique in that it transports warm waters to latitudes higher than in any other ocean, thereby producing the moderate climate of Europe. As far as it is known, the NADC exists as a "swath" or region, rather than an actual stream-like current, where the main thermocline shoals to the surface along which a stronger baroclinic transport is sustained than either the north or the south. A quiet, warm pool of water at the surface, its salinity can range between 35.2 and 35.7 ppt. A salinity maximum (>35.2) measured in the Faroe Bank Channel.It is the contribution of warm waters from the North Atlantic Drift current that is now understood to be the main moderating force of the climate over western Scandinavia, the UK and western Europe. At times of increased trade wind strength, tropical and subtropical waters are forced across the equator, enhancing the pool of warm water to be transferred to the high latitudes of the North Atlantic via the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Drift, thereby increasing the pull of the thermohaline convective conveyor. The increased supply of warm water to the polar regions of the northern hemisphere increases the ice-ocean moisture gradient and can accelerate ice sheet growth.
Tides
Europe has greatly affect oceans. The dates of spring tides and neap tides, approximately seven days apart, can be determined by the heights of the tides on the tide table: a small range indicates neaps and large indicates springs.
On the Atlantic coast of northwest Europe, the interval between each low and high tide averages about 6 hours and 10 minutes, giving two high tides and two low tides each day.The most extreme tidal range occurs around the time of the full or new moons, when the gravitational forces of both the Sun and Moon are in phase reinforcing each other in the same direction (new moon), or are exactly the opposite phase (full). This type of tide is known as a spring tide. During neap tides, when the Moon and Sun's gravitational force makes a right angle to the Earth's orbit, the difference between high and low tides is smaller. Neap tides occur during the first and last quarters of the moon's phases. The largest annual tidal range can be expected around the time of the Equinox, if coincidental with a spring tide.
Ice Cover
Europe has no ice cover.
Borders/Water/Bodies/Bordering/Oceans
It has a series of peninsulas named Eurasia. It is bordered in the north by the Arctic Ocean. The wind-driven North Atlantic surface current dominates Europe's western border and takes water northeast. To the north, the Norwegian Current takes water north toward the North Pole. The Zhem river is the eastern border. the north sea is in the margin of the Atlantic Ocean. Europe shares the Eurasian landmass with Asia. The traditional boundary between the two continents follows roughly the crest of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains, the Black Sea, the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, the Dardanelles, the Aegean Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Strait of Gibraltar. In the past other significant boundary lines included the line separating the European countries from the Soviet Union and the ideological boundary between Eastern (Communist) Europe and Western Europe that followed the eastern boundaries of Finland, West Germany, Austria, and Italy for the latter half of the 20th century. It is bordered in the west by the Atlantic ocean. It is bordered in the south by the Mediterranean sea. It is bordered by the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea between Europe and Asia.
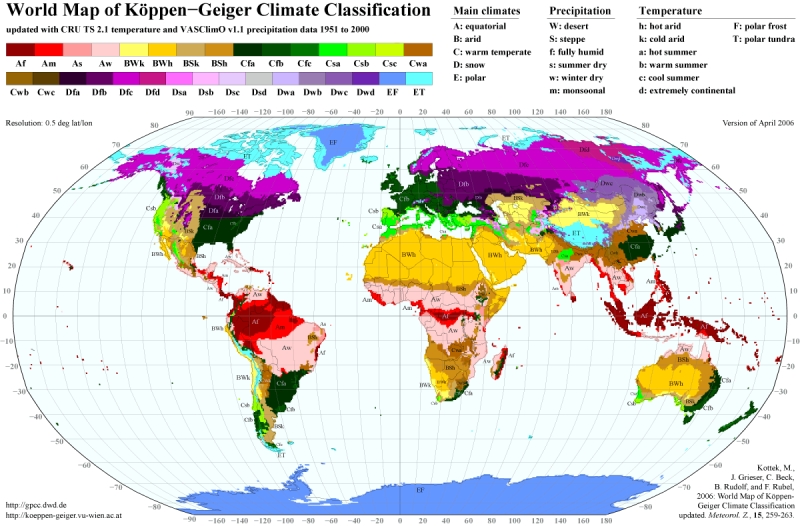
Climate
The climate of Europe is of a temperate, continental nature, with a maritime climate prevailing on the western coasts and a Mediterranean climate in the south. The climate is strongly conditioned by the Gulf Stream, which warms the western region to levels unattainable at similar latitudes on other continents. Western Europe is oceanic, while eastern Europe is continental and dry. Four seasons occur in western Europe, while southern Europe experiences a wet season and a dry season. Southern Europe is hot and dry during the summer months. The heaviest precipitation occurs downwind of water bodies due to the prevailing westerlies, with higher amounts also seen in the Alps. Tornadoes occur within Europe, but tend to be weak. The Netherlands and United Kingdom experience a disproportionately high number of tornado events.
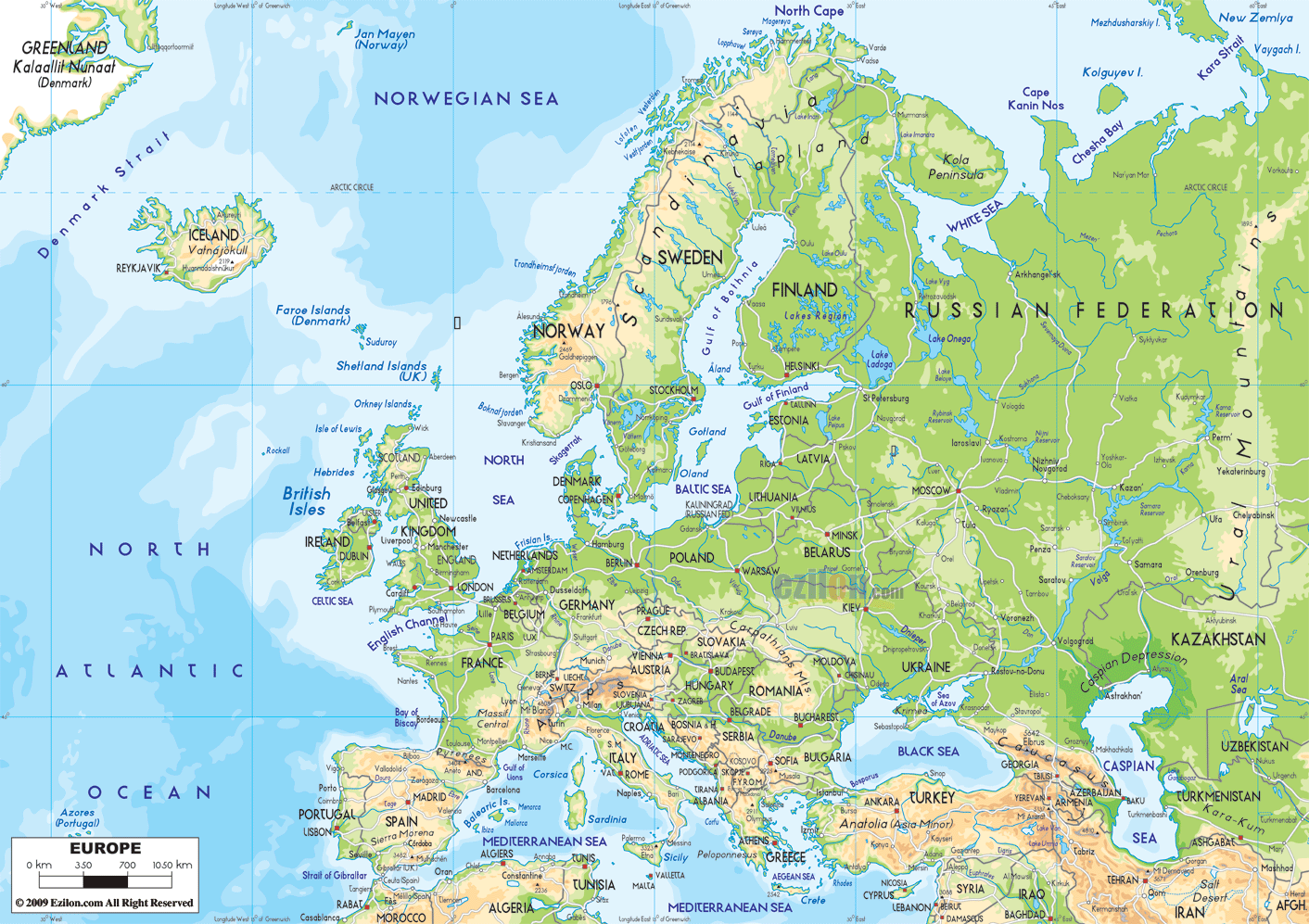
Physical Geography
The highest point is Mt. Elbrus(18,481 ft) located in the Caucasus and the lowest point, the surface of the Caspian Sea, is 92 ft below sea level. There are a few mountain ranges in Europe. The massive Alpine mountain range is divided into the Pyrenees, the Alps, the Carpathians, and the Balkans, traversing Europe from west to east.
Mineral Content
Germany has a lot of coal, some nickle, and some peat. Denmark has petroleum and natural gasses. Italy has coal, mercury and zinc. Greece has some iron ore, bauxite, some oil, lead and zinc. Spain and France share coal and zinc reserves, as well as copper and lead. France has uranium. Great Britain has some offshore reserves of oil and natural gas, as well as substantial coal reserves and some gold. Portugal boasts of some gold, as well as zinc, copper and uranium. Ireland has substantial reserves of natural gas and peat for fuel.Poland is blessed with substantial coal reserves, as well as natural gas, iron ore and copper reserves, as well as some limited supplies of silver . Serbia has some oil and natural gas, as well as copper and zinc. She also has some limited supplies of gold and silver.Bulgaria produces bauxite and copper. Russia has an abundance of natural resources. It has a large percentage of the world's oil and natural gas, as well as huge reserves of nearly all the most important strategic minerals valued today.Russia, Ukraine, and Sweden are among the world's major producers of iron ore. Copper, zinc, lead, bauxite, potash, sulfur, silver, and gold are also mined in a number of European countries. Ukraine is among the leading world producers of manganese, an alloy used in hardening steel.


http://school.eb.com/comptons/article-200435?query=europes%20mineral&ct=
http://www.ehow.com/about_5515777_list-european-natural-resources.html
Longitude and Latitude Ranges
Europe's exact northern border is located at 71 degrees north. The southern border is located at 34 degrees north. The western border is located at 10 degrees east. The eastern border is located at 40 degrees east.
Tectonic Plates
Europe lies mostly on the Eurasian plate. The northern part is mostly tectonically passive, except for a few shallow earthquakes around Greece. However, in the south of Europe, there is one region that is tectonically interesting, at least. In the south, there is an alternating boundary of oceanic transform faults and oceanic convergent boundary with some continental convergent boundaries. The Aegean Sea Plate lies north of the African Plate, and the African Plate is subducting under it. This causes the earthquakes around Greece. On the north end of the Aegean Sea Plate, there is a divergent boundary made with the Eurasian Plate. This divergent boundary made the Gulf of Corinth, in the middle of Greece. In the southeast, the Anatolia Plate covers most of the land. Its border is excessively complicated, with a subduction zone to the south and continental transform boundaries spread through most of the plate.
Volcanoes
Europe has nearly no volcanoes. one volcano is in Spain. This volcanic area is named Olot Volcanic Field. Volcano types: Pyroclastic cones Summit Elev: 893 m Basaltic lava. Latitude: 42.17°N Longitude: 2.53°E
Chaîne des Puys is in France. Volcano types: Cinder cones Lava domes Maars summit Elev: 1464 m Latitude: 45.775°N Longitude: 2.97°E
Italy has Vesuvius. Volcano types: Somma volcano Caldera Lava domes Summit Elev: 1281 m Latitude: 40.821°N Longitude: 14.426°E
Italy also has Stromboli. Volcano types: Strato volcano, Cinder cones Summit Elev: 924 m Latitude: 38.789°N Longitude: 15.213°E
Sicily has Etna. Volcano types: Stratovolcanoes Calderas Pyroclastic cones Summit Elev: 3350 m Latitude: 37.734°N Longitude: 15.004°E
Santorini is in greece. Volcano types: Shield volcanoes, Calderas, Lava domes. Summit Elev: 367 m Latitude: 36.404°N Longitude: 25.396°E
Links
Britannica: http://school.eb.com/comptons/article-9274228?query=Europe&ct=null
Britannica: http://school.eb.com/comptons/article-9274228?query=Europe&ct=null
Google Earth.
picture climate: http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/present.htm picture physical geography: http://www.ezilon.com/maps/europe-physical-maps.html
currents: http://oceancurrents.rsmas.miami.edu/atlantic/north-atlantic-drift.html