Earth Science 7 - Middle East2
Earth Science 7-Global Regions Index
Contents
Middle East
The Middle East is a region of the world east of Africa yet west of China. The Middle East is technically not defined as a continent, it is a part of Asia.
List of Middle Eastern Countries
- Afghanistan
- Algeria
- Bahrain
- Egypt
- India
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Jordan
- Kuwait
- Lebanon
- Libya
- Morocco
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia
- Somalia
- Syria
- United Arab Emirates
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Yemen
Latitude and Longitude Ranges
46N and 14N longitude. 78E and 27E latitude
Elevation Range
HIghest: 5610.148m above sea level (Mt. Damavand) Lowest: 396.24m below sea level (Dead Sea)
Bodies of Water
The Bodies of Water in the Middle East include:
- Indian Ocean
- Arabian Sea
- Gulf of Aden
- Caspian Sea
- Persian Gulf
- Gulf of Oman
- Red Sea
- Black Sea
- Mediterranean Sea
- Jordan River
- Dead Sea
- Euphrates River
- Tigris River
Bordering Oceans
- Indian Ocean
- North Equatorial Current
- Equatorial Countercurrent
- Zagros Mts
- Elburz Mts
- Caucasus Mts
- Rub Al Khali Desert
- BSk (steppe with mean annual temperature under 18 d. Celsius)
- BWk (desert with mean annual temperature under 18 d. Celsius)
- BWh (desert with mean annual temperature over 18 d. Celsius)
- Csa (Mediterranean with hottest month over 22 d. Celsius)
- Aw (hot, dry tropical, savanna)
- As (moist tropical, with dry season)
- Zuker
- Hanish
- Jabai Yar
- Jebel Zubai
- Harras of Dhamar
- Jabal el- Marha
- Jabal Haylan
- Harra es- Sawad
- Dallol
- Dalaffilla
- Dubbi
- Mallahie
- Gufa
- Asavyo
- Mousa Alli
- Jabal Hamman Demt
- Harrat al Birk
Map of Ocean Surface Temperatures (Celsius)

Water
Since water sources are becoming increasingly scarce, a majority of the Middle East's sanitary drinking water comes from desalinization the ocean.
Currents
The currents around the Middle East are:
Salinity
The Middle East has many Salt Lakes, like the Dead Sea. Not coincidentally, the Middle East also has many near landlocked lakes - lakes that have no tributaries or rivers flowing outward/inward. The Dead Sea, as with many Salt Lakes, has little water flowing into or out of it.
Topographic Features

Oil and Gas Deposits

Historically, the Middle East has had many oil and gas deposits
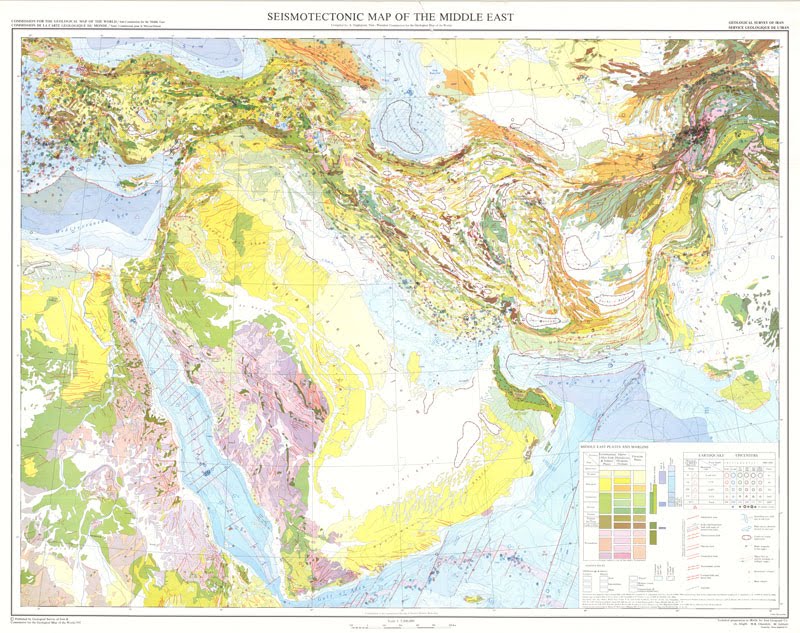
Geology
Geology Map of Middle East
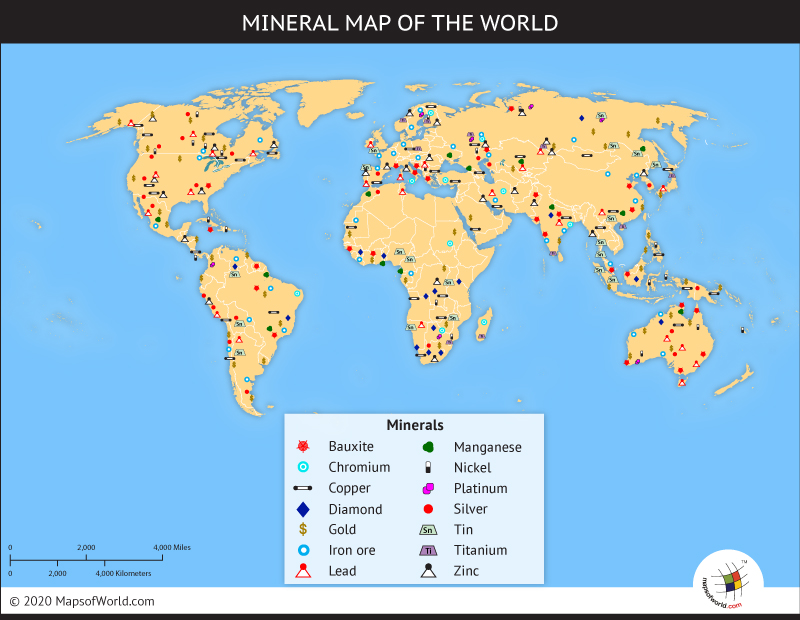
Minerals
One of the minerals that most people in the Middle East encounter every day is salt. The Middle East has many salt lakes, including the famous Dead Sea, which has a salt concentration of 33%.
Climate
Historically, the Middle East has had an arid climate with mild winters. Climate is hot and dry. Winters are mild with some rain. Hot desert conditions induce a strong seasonal wind pattern in the region, known as the monsoon (Arabic for season).
Koppen Climate Designation
The Middle Eastern Climate Types are:
Map of World Climate
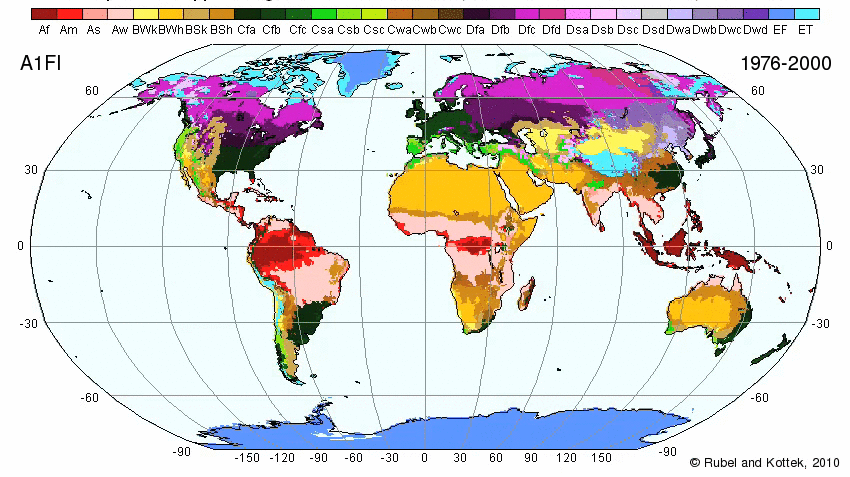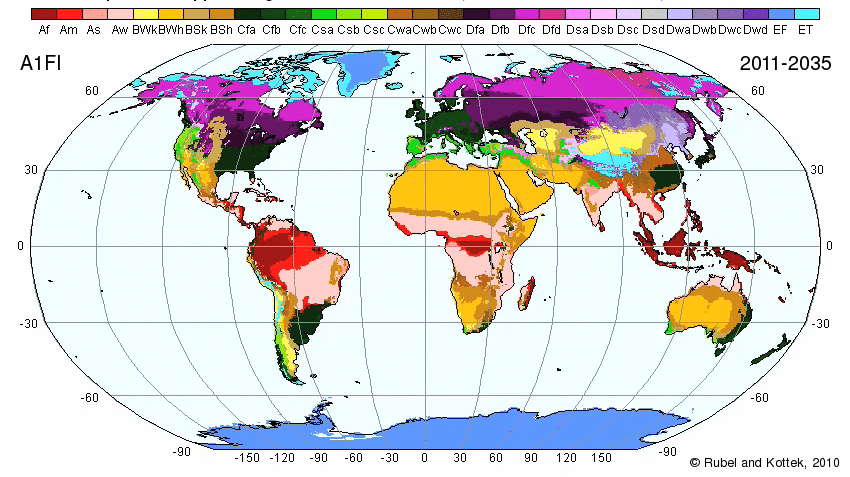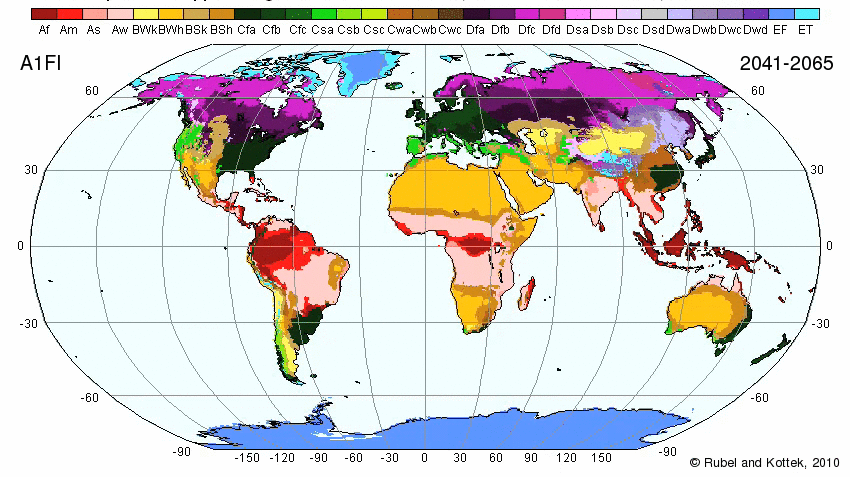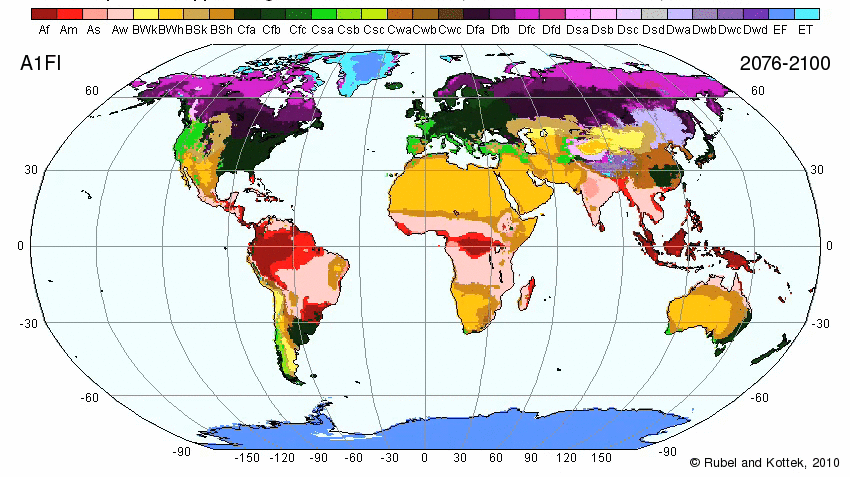
Plate Tectonics
Volcanoes
Most of the volcanoes in the Middle East region are hot spots, in the Indian Ocean, and rift-induced volcanoes on continental plates. 93% of the recorded eruptions have occurred on the Comoros Islands and Reunion Island. The shield volcano Piton de la Fournaise is the region's largest volcano. Some known volcanoes are:
Earthquakes
Recently, there was a earthquake located on the Turkey-Iran border with a magnitude of 4.2 and a depth of 10 kilometers. In eastern Turkey, on Fri. April 13, 2012, there was an earth with a magnitude of 4.2 and a a depth of 10.10 kilometers.
History of Significant Earthquakes in Middle East
Map
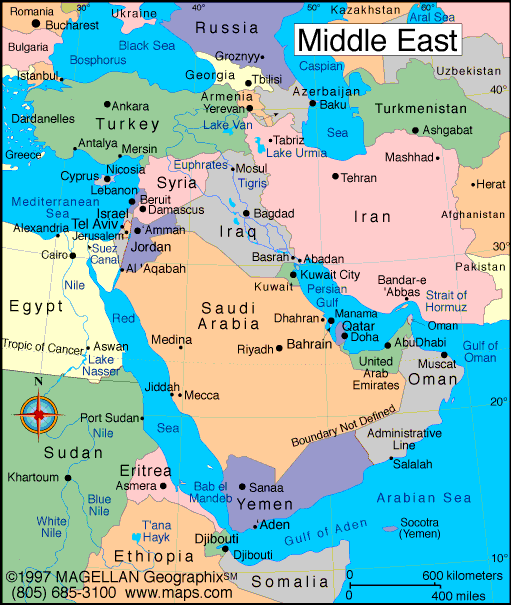
Links/References
[1] (Countries)(Oceans)
[2] (Bodies of Water)
[3] (Climate)
[4] (Climate Map)
[5] (Types of Climates)
[6] (Currents)
[7] (Ocean teamperatures)
[8] (About the Köppen Climate Classification System)
[9] (About Geology of Middle East)
[10] (Mineral Industries of Middle East in 2000)
[11] (World Mineral Map)
Siebert, L., Simkin, T., and Kimberly, P., 2010, Volcanoes of the World, 3rd ed. Berkeley: University of California Press, 568 p. (Volcanoes in the Middle East)