Earth Science 7 - Russia
Contents
Russia
Location
Russia is located at 60 00 N, 100 00 E, and it is one of the few countries which can be defined as being in the continents of Europe and Asia. It is bordering the countries of Mongolia and Kazakhstan.
Elevation Extremes
Russia’s elevation points are as follows: lowest point of elevation is the Caspian Sea at 28 m and the highest point is Gora El’brus at 5,633 m.
Geography
Russia’s terrain is hilly and plain-like. Russia is also the largest country in the world, if measured by area. Also, the highest point of elevation, Mt. El’brus is the highest peak in Europe.
Bodies of Water
Some of the bodies of water in Russia are the Caspian Sea, which is a sea, and many other major rivers. These include the Amur, the Lena, the Yenisey, and the Volga, which is the most famous river in Russia.
Topographic Features
Some of Russia’s notable geographic features are the hills of Ural and the forests of Siberia. Also, Russia houses Europe’s largest peak: Mount El’brus, which is 5,633 m high.
Bordering Oceans
The bodies of water that border Russia are the Sea of Okhotsk, the Black Sea, the North Pacific Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean.
.
Sources
Japan
Bodies of Water
Japan has many bays, but the most prominent is Tokyo Bay. There are also many bodies of water in Japan such as the Shinano, Tokachi and Mogami Rivers, Lake Kasumiguara and Lake Biwa.
Location
Japan is located at 36 00 N, 138 00 E, between the Pacific Ocean and the continent of Asia.
Geography
Japan is a hilly and mountainous country, and it suffers from many volcanic eruptions. It recently was struck by a horprific earthquake.
Elevation Extremes
The highest point in Japan is Fujiyama, which is at 3,776 meters above sea level. The lowest point is Hachiro-gata at -4 meters below sea level.
Topographic Features
Japan is situated in an area that makes it extremely vulnerable to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. Japan is an archipelago, which is a string of islands, and many of those islands are volcanic, including Iwo Jima.
Bordering Oceans
Sources
India
Climate
Averages
| Dehli Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 55 | 61 | 72 | 83 | 91 | 90 | 87 | 85 | 84 | 77 | 66 | 57 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 68 | 74 | 85 | 97 | 103 | 100 | 94 | 92 | 93 | 90 | 82 | 72 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 68 | 74 | 85 | 97 | 103 | 100 | 94 | 92 | 93 | 90 | 82 | 72 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 45 | 50 | 59 | 69 | 78 | 81 | 81 | 79 | 76 | 66 | 54 | 46 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Springar Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 34 | 40 | 48 | 57 | 65 | 72 | 76 | 74 | 68 | 56 | 45 | 37 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 43 | 49 | 59 | 69 | 77 | 84 | 86 | 85 | 82 | 72 | 60 | 48 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 27 | 32 | 39 | 45 | 52 | 59 | 66 | 64 | 55 | 43 | 34 | 29 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bombay Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 75 | 77 | 81 | 83 | 85 | 84 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 83 | 81 | 77 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 87 | 88 | 91 | 91 | 92 | 90 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 92 | 93 | 90 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 62 | 64 | 69 | 75 | 79 | 79 | 77 | 77 | 76 | 74 | 69 | 64 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 18 | 18 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bangalore Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 70 | 74 | 79 | 80 | 79 | 75 | 73 | 73 | 74 | 73 | 71 | 69 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 82 | 87 | 91 | 92 | 91 | 85 | 82 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 81 | 79 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 61 | 64 | 67 | 70 | 70 | 68 | 68 | 67 | 67 | 67 | 64 | 61 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 2 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hyderbad Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 72 | 77 | 84 | 88 | 90 | 84 | 79 | 78 | 78 | 77 | 75 | 71 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 84 | 90 | 97 | 100 | 102 | 94 | 88 | 86 | 87 | 87 | 85 | 83 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 78 | 75 | 72 | 71 | 71 | 69 | 64 | 58 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 11 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Imphal Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 57 | 62 | 69 | 74 | 76 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 76 | 72 | 66 | 59 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 72 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 83 | 79 | 73 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 41 | 46 | 54 | 63 | 67 | 71 | 72 | 71 | 70 | 63 | 55 | 44 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Koppen Scale
India has about nine different regions according to the Koppen Climate Scale. The different Regions are the Warm Semi-Arid (BWh), the Tropical Savanna (AW), the Temperate Contenental (Dfb), the Warm Desert (BWh), the Humid Subtropical (CWa) the Highland Subtropical (CWb)and the Warm Mediterranean (CSa).

Latitude's effect on Prevailing Winds

Because India is at about 10 to about 35 degrees north, the winds coming from India are the Prevailing North Easterlies.
 \
\
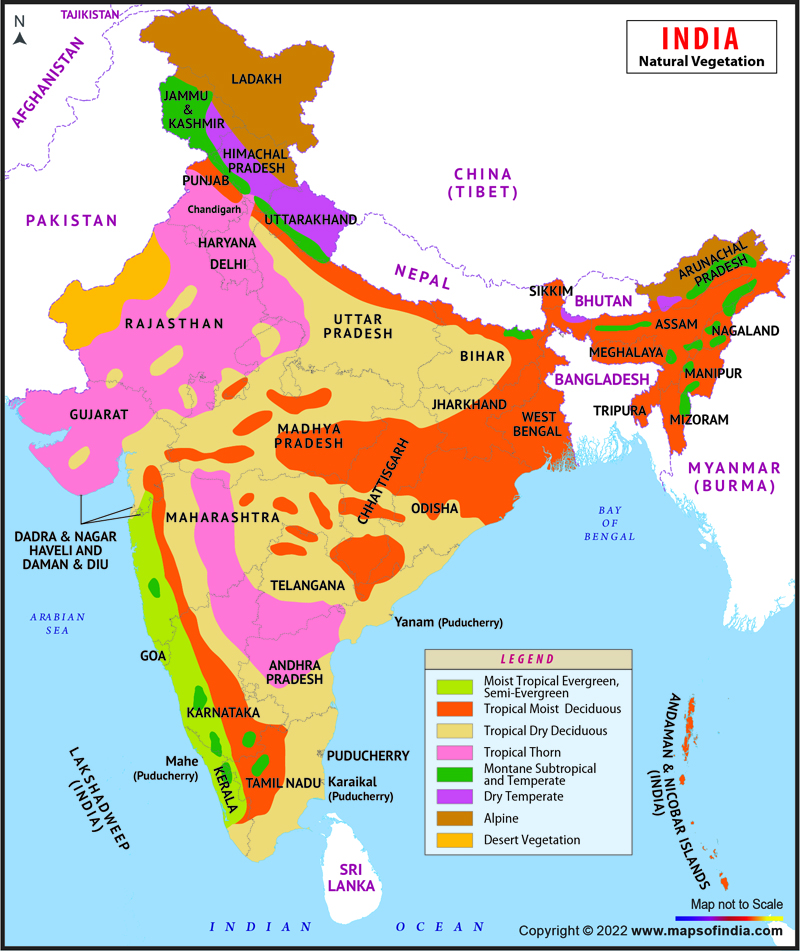
Vegitation Reletive to Elevation
 In northern India by the Himalayas, the vegetation is Alpine, in the
mainland of India ther is the Tropical Dry Decidous and Tropical Decidous Moist, in the north west of India there is the Tropical Thorn, and in the South West there is the Moist tropical Evergreen/Semi-Evergreen and Wet temperate, and near the Alpine there is also the Dry Temperate with Grasslands
In northern India by the Himalayas, the vegetation is Alpine, in the
mainland of India ther is the Tropical Dry Decidous and Tropical Decidous Moist, in the north west of India there is the Tropical Thorn, and in the South West there is the Moist tropical Evergreen/Semi-Evergreen and Wet temperate, and near the Alpine there is also the Dry Temperate with Grasslands
High and Low Pressure Zones with Topography
India has diverse topography. In the North where it has mountains there are low pressure zones because the air is sinking after the wind blows it off the mountain. In the south there are deserts coming off the mountains these are high pressure zones. In the west of India the rolong plains are low pressure because there is rain coming down to vegetate them.
. 
Proximity to water to Ocean Currents
India is partley on the coast line and the currents flow underneath it's tip oceanmotion.org/images/oceancurrents.gif
Bodies of Water
Large bodies that border India are the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengals, and the Indian Ocean.
Latitude and Longitude
""The Coordinates are 20N, 77E."".
Elevation Range
""The lowest point is the Indian Ocean at 0 m The highest point is Kanchenjunga at 8,598 m""
Topographical features
In the north of India the largest mountain range in the world exists, the Himalayan Mountain Range. In the south of India there are deserts. In the west there are rolling plains.
India Lies between China, Burma, Nepal, Bhutan and Pakistan.
Philippines
Climate
Koppen Scale
The Philippines has manly two regions, the

Averages in Manila
| Manila Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 80 | 81 | 83 | 86 | 85 | 84 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 80 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 85 | 87 | 89 | 92 | 91 | 90 | 87 | 88 | 87 | 88 | 87 | 85 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 75 | 76 | 77 | 80 | 80 | 79 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 77 | 75 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 13 | 13 | 17 | 6 | 6 | 5 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Averages in Puerto Princesa AFB
| Puerto Princesa AFB Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 80 | 80 | 81 | 83 | 82 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 80 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 87 | 87 | 88 | 90 | 90 | 89 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 86 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 74 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 76 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 74 | ||
| Avg. Rain Days | 3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 5 | ||
| Avg. Snow Days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Averages in Legapazi
| Legapazi Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
| Avg. Temperature | 78 | 78 | 80 | 82 | 83 | 83 | 81 | 82 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 79 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 83 | 84 | 86 | 88 | 90 | 89 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 88 | 86 | 84 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 73 | 73 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 77 | 76 | 76 | 76 | 75 | 75 | 74 | ||
Lattitude to Prevailing Winds
.svg/250px-The_Philippines_and_ASEAN_(orthographic_projection).svg.png) The Philippines is between 7 degrees and 15 degrees. It is very close to the equator so the winds come from the Easterly trade winds
The Philippines is between 7 degrees and 15 degrees. It is very close to the equator so the winds come from the Easterly trade winds
Elevation to Vegitation
The elevation is almost the same in most places and ther is lots of rainforests that grow in those areas.
Topography to high and low pressure zones
It is a low pressure zone because the air is sinking at that latitude.
Proximety to Currents
The currents curve away from the Philippines.

Bodies of Water
The Philippines consists of grouped islands in the Indian Ocean. [[1]]
Elevation Range
The lowest point is the Philippine Sea 0 m The highest point is Mount Apo 2,954 m
Latitude and Longitude
13 00 N, 122 00 E
Topographical features
It is an archipelago and it is on a fault line
China
The Zhonghua Renmin Gongheguo (People’s Republic of China), is located in Eastern Asia, bordering the East China Sea, Korea Bay, Yellow Sea, and South China Sea, between North Korea and Vietnam. At 35’00” N, 105’00” E, China contains Template:H:title in total; Template:H:title of land and Template:H:title of water. Slightly smaller than the US, China has the largest population of any country in the world, boasting over 1.3 billion citizens. The total population is 1,336,718,015, largest compared to other countries in the world. The country’s most populous cities are Shanghai at 16.575 million, Beijing at 12.214 million, Chongqing at 9.401 million, Shenzhen at 9.005 million, and Guangzhou at 8.884 million.
Geography
China is the world’s fourth largest country in total land and water, after Russia, Canada, and the US. It borders Afghanistan, Bhutan, Burma, India, Kazakhstan, North Korea, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Vietnam for a total of Template:H:title. Its coastline is Template:H:title km long and claims Template:H:title of territorial sea, Template:H:title of shared sea, and Template:H:title of exclusive economic zone. Mt. Everest, on the border with Nepal, is the world’s tallest peak.
Several large bodies of water surround China. They are the South China Sea, Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan, and the Pacific Ocean.[10] The Yangtze and Yellow Rivers are the third- and sixth- longest in the world and are home to a variety of species of plant and animal life.
Climate
The Climate of China is extremely diverse, because of the fact that it is quite tropical in southern China from the river-valley areas near the Yangtze River, Yellow River, and others, but subarctic in the north from the Himalayas. The lowest point in China is Turpan Pendi at Template:H:title below sea level, and Mt. Everest claims its highest point at Template:H:title above sea level and counting. [11]The temperature varies from around Template:H:title to about Template:H:title, from the Himalayas to the Wuhan, Chongqing, and Nanjing Rivers, along with the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers.[12]
Natural Disasters
China is prone to frequent typhoons (about 5 per year along the southern and eastern coasts), damaging floods, tsunamis, earthquakes, droughts, land subsidence, and volcanism, though most haven’t been active for more than a century. They include Changbaisha, Hainan Dao, and Kunlun. Changbaisha, a.k.a. Baitoushan, Baegdu, or P’aektu-san, is home to Heaven Lake, a caldera left behind by a major eruption in 969 AD, ± 20 years that filled up with rainwater. Among the stranger findings are sinkholes. Often referred to as “tiankeng” or skyholes, sinkholes have appeared throughout the world, most recently in China. In one instance, sinking land has created an enormous hole in front of an elementary school and swallowed an entire playground in Ningxiang county in China's Hunan province, the Associated Press reports. The sinkhole started to yield in mid-January, at first forming a hole twenty meters in diameter. Intense springtime rainfall has since accelerated the hole's expansion, which has, in turn, caused damage to area buildings.[13]
Natural Resources
China contains an abundance of natural resources, including coal, iron ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten, antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead, zinc, rare earth elements, uranium, and has the world’s largest hydropower potential.
China’s exports of raw products/material include electrical and other machinery, including data processing equipment, apparel, textiles, iron and steel, and optical and medical equipment.
It imports electrical and other machinery, oil and mineral fuels, optical and medical equipment, metal ores, plastics, and organic chemicals.
China is a world leader in gross value of agricultural output − rice, wheat, potatoes, corn, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, apples, cotton, oilseed, pork, and fish.
Also, it is the world leader in gross value of industrial output – mining and ore processing, iron, steel, aluminum and other metals, coal, machine building, armaments, textiles and apparel, petroleum, cement, chemicals, fertilizers, consumer products such as footwear, toys and electronics, food processing, transportation equipment including automobiles, rail cars and locomotives, ships, and aircraft, telecommunications equipment, commercial space launch vehicles, and satellites.
14.86% of the land in China is farmable, 1.27% of it is used for permanent farming, and 83.87% of the land is used to build and expand suburban communities, cities, and such. Template:H:title of land in China is irrigated, and 2,829.6 cu km of water is renewable. [14]
Biodiversity
In China, the regional area of the mountains in the southwest, by far, contains the most types of species, in both plants and animals. China has a wealth of biodiversity, with the largest amount of bird species and gymnosperm variation in the world, but it faces a grave situation: in just the southwest mountains, 15-20% of higher plant varieties are endangered, pressuring the existence of the 40.00 species of organisms related with them. But China has good news: since 1500 CE, no recorded species have ever gone extinct in that area. The Mountains of Southwest China, with Template:H:title of protected land and Template:H:title of higher leveled protection of land, has taken part in an ongoing effort, like all countries, to preserve biodiversity, stop climate change, and keep the environment clean. The number of endangered plant species and frightening, with about 3,500 species endangered. In late 2010, China revealed an aggressive plan to protect biodiversity. The plan was to divide 23% of the country into 35 priority conservation areas and to set a target of controlling biodiversity loss by 2020. Although helpful, this is too late, considering that already, the panda, the snow leopard, and the red panda are critically endangered. [15]
Environment
China’s air quality is at fault, as it contributes to smog and acid rain. Air pollution (greenhouse gases, sulfur dioxide particulates) from reliance on coal produces the acid rain. China also suffers from the occasional water shortage, particularly in the north; water pollution from untreated wastes; deforestation; and an estimated loss of one-fifth of agricultural land since 1949 to soil erosion and economic development; desertification; and trade in endangered species. [16]
Global Environmental Treatises
China is a party of the Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Biodiversity, Law of the Sea, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, and Ozone Layer Protection, and attempts to preserve Wetlands, and Endangered Species. It acts to prevent Marine Dumping, Climate Change, Desertification, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Ship Pollution, and Whaling. [17]
Energy
Electricity
- Production
- 3.446 trillion kWh (2nd country in world)
- Consumption
- 3.438 trillion kWh (2nd country in world)
- Exports
- 17.39 billion kWh
- Imports
- 11.38 billion kWh
Oil
- Production
- 4.273 million bbl/day (4th country in the world)
- Consumption
- 9.189 million bbl/day (3rd country in the world)
- Exports
- 480,600 bbl/day (30th country in the world)
- Imports
- 4.753 million bbl/day (3rd country in the world)
- Proved Reserves
- 20.35 billion bbl\day (14th country in the world)
Natural Gas
- Production
- 94.41 billion cu m (8th country in the world)
- Consumption
- 106.7 billion cu m (5th country in the world)
- Exports
- 4.02 billion cu m (29th country in the world)
- Imports
- 16.33 billion cu m (17rd country in the world)
- Proved Reserves
- 3.03 trillion cu m (13th country in the world) [18]
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/rs.html
- ↑ http://kids.britannica.com/comptons/article-207540/Russia
- ↑ http://novaonline.nvcc.edu/eli/evans/HIS241/Notes/Geography/Geography.html
- ↑ http://www.wepa-db.net/policies/state/japan/japan.htm
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ja.html
- ↑ http://www.climate-zone.com/climate/india/
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
- ↑ http://www.climate-zone.com/climate/philippines/
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
- ↑ Google Earth
- ↑ http://climate-charts.com/World-Climate-Index-Map.html World Climate Map
- ↑ http://climate-charts.com/World-Climate-Maps.html World Climate Map (2)
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/111803/China Britannica Encyclopedia
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html CIA Factbook
