History of Computers - RFID
Page created by Michael He
RF-ID's are small metal identification tags which produce unique electromagnetic fields that are read by a receiver. Although they were first introduced in 1945 by Léon Theremin in the Soviet Union, these early RF-ID's were used mainly in military aircraft to determine friendlies from foe or for espionage. They became widespread in the consumer market in 2005. [1]
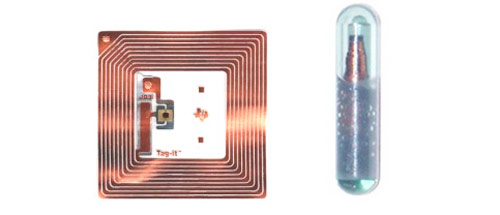
Types
RF-ID tags can be either passive, in which the receiver emits a signal which reads the RF-ID tag, or active such as transponders that emit a signal to be picked up by a receiver. The benefit of the active tags is that they are battery powered and have a longer range than passive RF-ID's. However, the passive tags are very small, some the size of a grain of rice, allowing for them to be placed almost anywhere such as inside clothing and on packages.
Uses
RF-ID tags are used almost anywhere where tracking objects is of primary importance. Passive RF-ID's are used in libraries inside the books to allow for rapid processing of the books, in distribution centers, where they are placed on packages coming in and out of the center and toll collection booths to name a few [2]. Active, RF-ID's are used in car keys to unlock the car just by being near it and in airplanes, where they need to constantly be broadcasting their flight number.
Significance
RF-ID's are a fast and inexpensive way to identify and track objects with average prices of $0.90 per tag, although the receiver is more expensive. The market for the tags is worth $10.1 billion, up from $9.5 billion in 2014 and $8.8 billion in 2013 [3], demonstrating a significant market for the tags. Multiple tags can be read at once, allowing for increased processing speeds, resulting in for more efficient operation of the task at hand. Finally, there does not need to be a direct line of sight as with bar code scanners, allowing for more convenient ways of applying the tag.
External Links
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio-frequency_identification
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L%C3%A9on_Theremin
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transponder
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barcode_reader