India/Middle East 8
Contents
- 1 India and the Middle East
- 2 Major Seas-Middle East :
- 3 The Latitude and Longitude Regions-Middle East:
- 4 Elevation Range-Middle East
- 5 Large Bodies of Water-Middle East
- 6 Topographic Features-Middle Est
- 7 Bordering Oceans-Middle East
- 8 Major Bodies of Water-India
- 9 Latitude and Longitude Coordinates-India
- 10 Topographic features-India
- 11 Bordering Oceans-India
- 12 Average Monthly Temperature and other climate stuff India
- 13 Average Temperature Middle East
- 14 Average Precipitation Middle East
- 15 Latitude-Middle East
- 16 Elevation-Middle East
- 17 Topography- Middle East
- 18 Prevailing Winds-Middle East
- 19 Vegetation-Middle East
- 20 High and Low Pressure Zones-Middle East
- 21 Geology
- 22 Types of Rocks Found in the Middle East
- 23 Types of Rocks Found in India
- 24 Major Minerals of the Middle East
- 25 Major Minerals of India
- 26 Tectonic Plates
- 27 Earthquakes
- 28 Volcanoes
- 29 Rocks' Relation to Tectonic Activity
- 30 Links
India and the Middle East
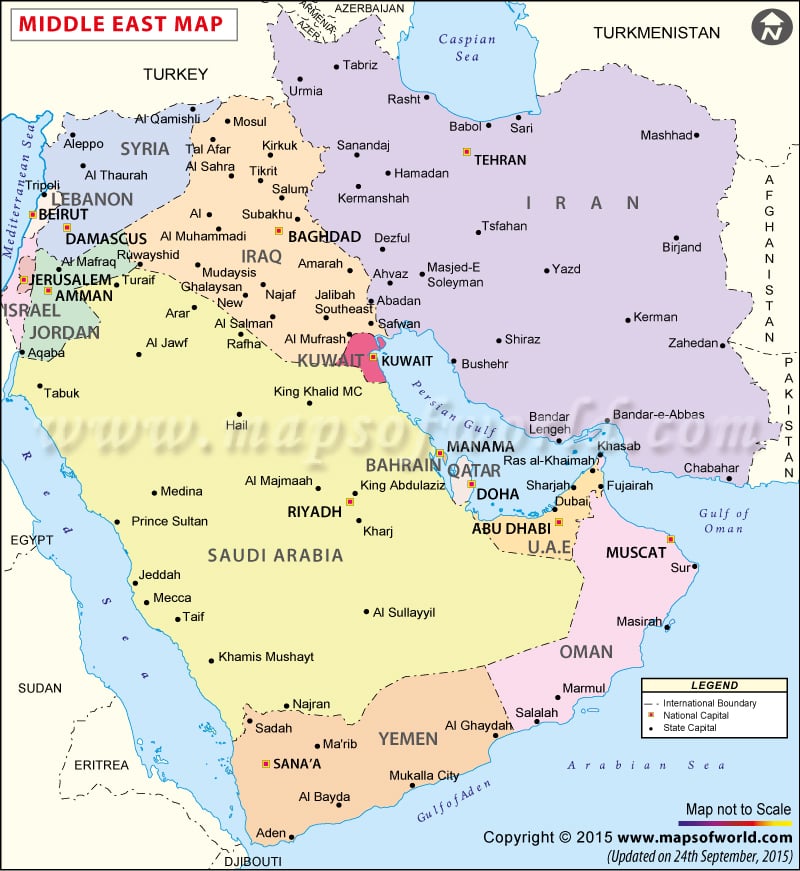
Countries-Middle East: Egypt Iran Turkey Sudan Algeria Morocco Iraq Saudi Arabia Yemen Syria Israel Libya Jordan United Arab Emirates Lebanon Palestinian territories Kuwait Oman Qatar Bahrain
Major Seas-Middle East :
Red Sea Gulf of Aqaba Arabian Gulf [1]
The Latitude and Longitude Regions-Middle East:
Latitude: 30 (N) Longitude: 45 (E)
Elevation Range-Middle East
Lowest: The Dead Sea on the boarder of Israel and Jordan in the Middle its height is 1,388 ft below sea level Highest: Pik Samani at 24,590 ft
Large Bodies of Water-Middle East
Dead Sea Mediterranean Sea Black Sea Red Sea Caspian Sea Arabian Sea
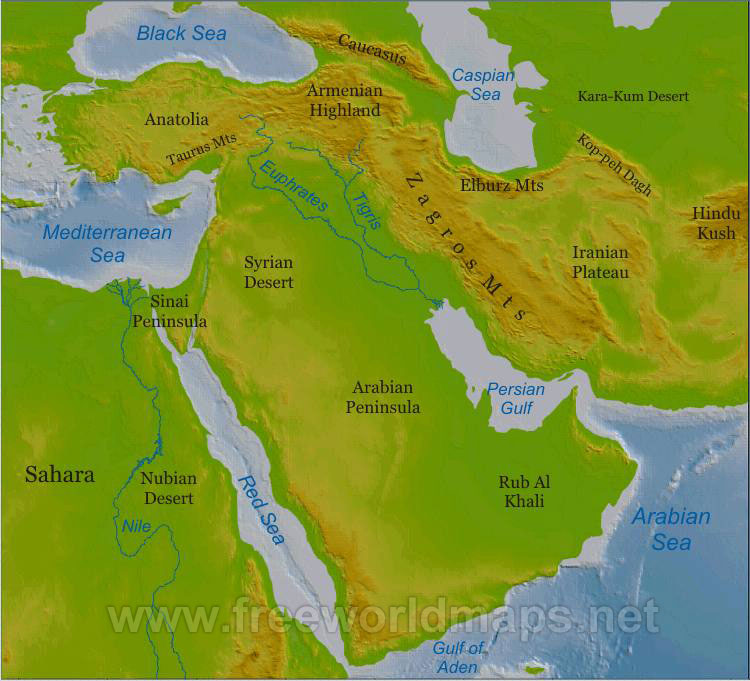
Topographic Features-Middle Est
Rub al Khali dessert Caucasus Mts Elbruz Mts Zagros Mts
Bordering Oceans-Middle East
Indian Ocean
Major Bodies of Water-India
Ganges River
Latitude and Longitude Coordinates-India
20 00 N, 77 00 E [2]
Topographic features-India
Deccan Plateau
Bordering Oceans-India
Bay of Bengal Arabian Sea Laccadive Sea [3]
Average Monthly Temperature and other climate stuff India
| New Delhi,India Temperature in Farenheit | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual | ||
| Avg. Temperature F | 58 | 63 | 73 | 84 | 91 | 92 | 87 | 86 | 85 | 79 | 69 | 60 | 77 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 68 | 73 | 83 | 95 | 101 | 101 | 93 | 91 | 92 | 90 | 81 | 71 | 87 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 48 | 53 | 62 | 72 | 80 | 83 | 81 | 80 | 78 | 68 | 57 | 49 | 68 | ||
Climate zones: BWh-Hot desert climates BSh-Hot semi-arid climates Cwa-Humid subtropical climate Am-Tropical monsoon climate
The latitude of Delhi, India is 28 35N. The average elevation of India is about 350ft above sea level. The climate zones of India are BWh-Hot desert climates, BSh-Hot semi-arid climates, Cwa-Humid subtropical climate, Am-Tropical monsoon climate. West coasts of continents in tropical and subtropical latitudes (except close to the equator) are bordered by cool waters. Their average temperatures are relatively low with small diurnal and annual ranges. There is fog, but generally the areas (southern California, Mo-rocco, etc.) are arid. West coasts of continents in middle and higher latitudes are bordered by warm waters which cause a distinct marine climate. They are characterized by cool summers and relatively mild winters with a small annual range of temperatures (upper west coasts of the United States and Europe). The average monthly rainfall of the Panta climate zone is 3.267 inches, the average monthly rainfall of the Delhi is 2.308 inches. Here is the topography map. The prevailing winds for Dehli are JAN-4, FEB-4, MAR-5, APR-6, MAY-8, JUN- 6, JUL-6 AUG- 6, SEP-6, OCT- 5, NOV- 3, DEC-4. Most of India is tropical Dry, but some is tropical Thorn. Not many variations in pressure except when the altitude is 6,000ft. The Asiatic Monsoon influences the currents of the North Indian Ocean, while the currents of the South Indian Ocean are influenced by the atmosphere’s anticyclone circulation.
Average Temperature Middle East
| Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Avg. Temperature | 48 | 54 | 62 | 72 | 82 | 90 | 94 | 92 | 86 | 76 | 61 | 52 | 72 |
| Avg. Max Temperature | 58 | 64 | 73 | 84 | 96 | 105 | 110 | 108 | 103 | 91 | 74 | 62 | 86 |
| Avg. Min Temperature | 38 | 43 | 50 | 59 | 68 | 74 | 78 | 75 | 70 | 60 | 47 | 42 | 59 |
| Tehran, Iran (BSk) Average Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Avg. Temperature | 35 | 41 | 50 | 63 | 71 | 82 | 88 | 85 | 79 | 66 | 53 | 42 | 64 |
| Avg. Max Temperature | 29 | 34 | 42 | 54 | 62 | 72 | 78 | 76 | 70 | 58 | 45 | 36 | 55 |
| Avg. Min Temperature | 29 | 34 | 42 | 54 | 62 | 72 | 78 | 76 | 70 | 58 | 45 | 36 | 55 |
The latitude of Delhi, India is 28 35N. The average elevation of India is about 350ft above sea level. The climate zones of India are BWh-Hot desert climates, BSh-Hot semi-arid climates, Cwa-Humid subtropical climate, Am-Tropical monsoon climate. West coasts of continents in tropical and subtropical latitudes (except close to the equator) are bordered by cool waters. Their average temperatures are relatively low with small diurnal and annual ranges. There is fog, but generally the areas (southern California, Mo-rocco, etc.) are arid. West coasts of continents in middle and higher latitudes are bordered by warm waters which cause a distinct marine climate. They are characterized by cool summers and relatively mild winters with a small annual range of temperatures (upper west coasts of the United States and Europe). The average monthly rainfall of the Panta climate zone is 3.267 inches, the average monthly rainfall of the Delhi is 2.308 inches. Here is the topography map. The prevailing winds for Dehli are JAN-4, FEB-4, MAR-5, APR-6, MAY-8, JUN- 6, JUL-6 AUG- 6, SEP-6, OCT- 5, NOV- 3, DEC-4. Most of India is tropical Dry, but some is tropical Thorn. Not many variations in pressure except when the altitude is 6,000ft. The Asiatic Monsoon influences the currents of the North Indian Ocean, while the currents of the South Indian Ocean are influenced by the atmosphere’s anticyclone circulation.
| Tripoli, Lebanon(Csa) Average Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Avg. Temperature | 55 | 55 | 57 | 62 | 67 | 74 | 77 | 80 | 76 | 71 | 67 | 59 | 66 |
| Avg. Max Temperature | 61 | 61 | 64 | 69 | 74 | 80 | 83 | 86 | 82 | 79 | 66 | 60 | 73 |
| Avg. Min Temperature | 49 | 49 | 50 | 55 | 61 | 68 | 71 | 74 | 70 | 64 | 59 | 53 | 60 |
Average Precipitation Middle East
| Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Precipitation | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Precipitation (inches) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1 | 6.1 |
| Tehran, Iran (BSk) Average Precipitation | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Precipitation (inches) | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1.2 | 9.3 |
Latitude-Middle East
Because the Middle East's latitude is mostly near the Equator, it gets a pretty direct angle of isolation. This cuases the temperatures, in the lower countries espicially, to be warmer.
Elevation-Middle East
The elevation of most of the Middle East is between 501-1,500 in the West or between 251-(-407) meters in the East above sea level. For every 1000 feet above sea level the temperature decreeses 4 degrees. This causes colder temperatures in the West to be cooler, but the tmeperautures in the East warmer.
Topography- Middle East
The Rub al Khali is a large desert in the Middle East where the average maximum daily temperature is about 47 degrees celsius. Mt. Elbrus is the highest point in the Middle East, the average temperature there (in the valley) is 20 degrees celsius. [7] [8] [9]
Prevailing Winds-Middle East
Prevailing winds don't affect the Middle East much.
Vegetation-Middle East
There isn't much vegetation in the Middle East. Most of it is desert scrub. [10]
High and Low Pressure Zones-Middle East
The Middle East is currently near a high pressure zone in Asia. This means that wind and storms are blown into the area. [11]
Geology
Types of Rocks Found in the Middle East
Sedimentary rocks form from sediments being compacted and cemented together. Sand, for example, can be compacted into fine grained sedimentary rocks. There are a lot sedimentary rocks in the Middle East because of all the deserts. Metamorphic rocks form from an igneous, sedimentary, or another metamorphic rock being subjected to high heat and pressure. When tectonic plates push against each other to form mountains there is a lot of heat and pressure forming metamorphic rocks. There are also metamorphic rocks from when the mountains formed. [12]
Types of Rocks Found in India
Along with forming in deserts, sedimentary rocks also form in rivers. When sediments are uplifted they are carried down river where they settle. The larger sediments typically settle near the head of the river and the smaller sediments typically settle in calmer waters near the end. India has a lot of sedimentary rocks because of all the rivers. Like the in Middle East, the Southern part of India has a few mountain ranges. [13]

Major Minerals of the Middle East
Metals- The Middle East region accounted for 12% of the world’s chromite production, 7% of the world’s aluminum production, and 3% of the world’s crude steel production. Crude steel production in the Middle east region decreased to 42.3 Mt in 2009 compared with 44 Mt in 2008.
Industrial Minerals- The Middle East region accounted for 17% of the world’s gypsum production, 14% of the world’s potash production, and 7% of the world’s ammonia, cement, and phosphate rock production. In 2009, the volumes of potash and phosphate rock production decreased significantly compared with that of 2008 owing to the decreased demand that resulted from the financial crisis that affected most of the world in 2009.
Mineral Fuels- The Middle East region production of crude oil accounts for 29% of the world’s total crude oil production. The region is responsible for 13.6% of the world’s natural gas production. The main type of oil found in the region is petroleum. [14]
Major Minerals of India
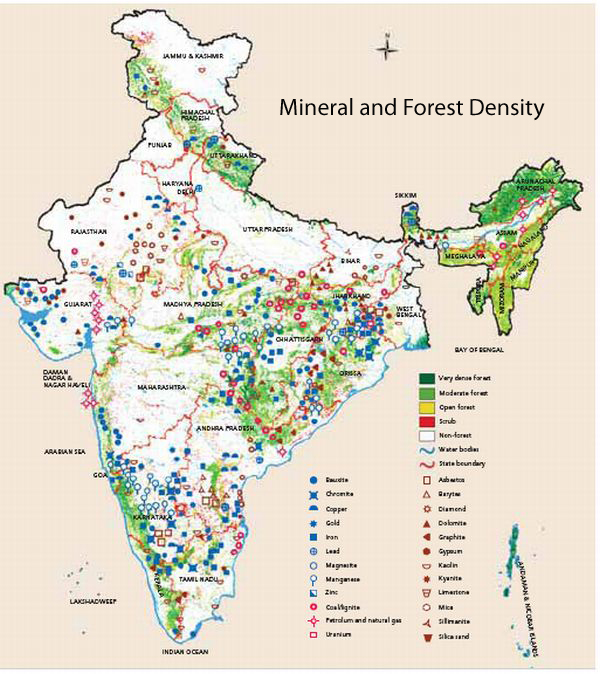
Metal- In India the metals produced are copper, produced 394,000 tons, iron, produced 8,120,00, manganese, and titanium.
Industrial Minerals- Graphite has a capacity of 10,000 ton/yr of processed graphite from five mines—Beharamunda, Deharmunda, Dudkamal, Gandabhali, and Temrimal. Also diamond, produces 27.4 million carrots, and cement are also a part of India's industry.
Mineral Fules- As well as the minerals above, India produces many fuels such as coal, natural gas, petroleum, and uranium.
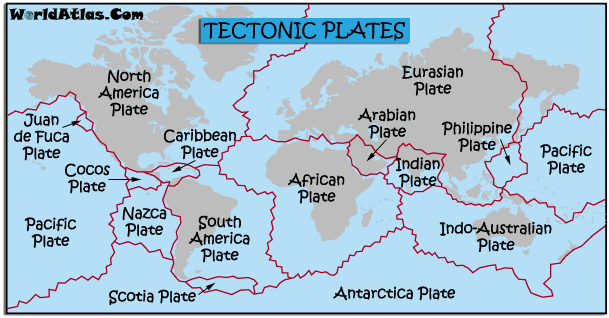
Tectonic Plates
Middle East: African Plate- Boundaries: North-Divergent,west-convergent, east-divergent,south-uncertain Arabian Plate-Boundaries: west/northwest-divergent, northeast-convergent,southeast-divergent , Eurasian Plate- Boundaries: west/north/southwest corner-divergent, most of south/southeast-convergent, northeast-uncertain
India: Indian Plate- Boundaries:Northeast is a convergent boundary, Southeast is an uncertain, the western boundary is divergent
Margin: African Plate: Active-North, Passive-everywhere else Arabian Plate: Active-all sides, Passive-nowhere Eurasian Plate: Active-South/South East, Passive-North/West Indian Plate: Active-North/East/West, Passive-South
Earthquakes
There are not many earthquakes in The Middle East and Asia. There are no earthquakes listed in Egypt, but there have been two earthquakes in Northwestern India. • Earthquake #1 was in 1995, it had a magnitude of 7.3 and its depth was 10. • Earthquake #2 was in 1993, it had a magnitude of 6.1 and its depth was 10. There have been many earthquakes all over the right side of the Middle East. • Earthquake #1 was in 1997, it had a magnitude of 6.1 and its depth was 10. North Iran. • Earthquake #2 was in 1990, it had a magnitude of 7.7 and its depth was 18. North Iran. • Earthquake #3 was in 2004, it had a magnitude of 6.3 and its depth was 17. Middle-North Iran. • Earthquake #4 was in 2002, it had a magnitude of 6.5 and its depth was 10. Middle Iran. • Earthquake #5 was in 1997, it had a magnitude of 7.1 and its depth was 10. East Iran. • Earthquake #6 was in 1997, it had a magnitude of 7.7 and its depth was 10. East Iran. • Earthquake #7 was in 1988, it had a magnitude of 6.1 and its depth was 33. Southwest Iran. • Earthquake #8 was in 1999, it had a magnitude of 6.3 and its depth was 33. Southwest Iran. • Earthquake #9 was in 1994, it had a magnitude of 6.1 and its depth was 12. Southwest Iran. • Earthquake #10 was in 1994, it had a magnitude of 6.3 and its depth was 9. East Iran. • Earthquake #11 was in 1996, it had a magnitude of 6.3 and its depth was 9. East Iran. • Earthquake #12 was in 1994, it had a magnitude of 6.1 and its depth was 6. East Iran. • Earthquake #13 was in 1990, it had a magnitude of 6.7 and its depth was 10. South Iran. • Earthquake #14 was in 1999, it had a magnitude of 6.6 and its depth was 33. South Iran. • Earthquake #15 was in 2003, it had a magnitude of 6.8 and its depth was 10. South Iran. • Earthquake #16 was in 1998, it had a magnitude of 6.9 and its depth was 9. South Iran. • Earthquake #17 was in 2005, it had a magnitude of 6.5 and its depth was 14. South Iran. • Earthquake #18 was in 1997, it had a magnitude of 8.1 and its depth was 12. Southwestern Iran.
Volcanoes
The Middle East and India has may volcanoes. Off the coast of South/East India, there is a shield volcano with basaltic magma. The boundary is uncertain. On the South/Western side of the Arabian Plate there many composite/stratovolcano volcanoes which produce andesitic magma, many including calderas. on the Southern side of the Eurasian Plate are more composite/stratovolcano volcanoes, also producing andesitic magma. In between the Eurasin and Arabian plates is a convergent boundary which results in volcanoes.
Rocks' Relation to Tectonic Activity
Where the plates have formed volcanoes, there are a lot of igneous rock because of the magma. Metamorphism occurs at convergent plate boundaires and forms metamorphic rocks.
Links
- ↑ http://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
- ↑ http://www.weatherbase.com/search/search.php3?query=new+delhi+india+snow
- ↑ http://www.weatherbase.com
- ↑ http://www.weatherbase.com
- ↑ http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/pa/pa1303_full.html
- ↑ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/melnd.htm
- ↑ http://www.kilimanjaro.cc/elbrus2.htm
- ↑ http://www.gperfors.com/Middle%20East%20Vegetation.htm
- ↑ http://www.findlocalweather.com/weather_maps/pressure_middle_east.html
- ↑ http://www.google.com/imgres?q=geographic+map+of+the+middle+east&um=1&hl=en&sa=N&biw=1280&bih=709&tbm=isch&tbnid=wS9bexjt8qBxGM:&imgrefurl=http://www.freeworldmaps.net/middleeast/physical.html&docid=s8a64KK01959TM&imgurl=http://www.freeworldmaps.net/middleeast/middle-east-physical-map.jpg&w=750&h=681&ei=OkVFT5qNDeK3sQKL-_XCDw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=560&vpy=246&dur=406&hovh=163&hovw=180&tx=153&ty=87&sig=108409308492285192863&page=1&tbnh=123&tbnw=135&start=0&ndsp=22&ved=0CFcQrQMwAw
- ↑ https://encrypted-tbn1.google.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcToa0BF4NqH1KHDTom0Sjb2oPflgotqmC5hEpYwRTzHqY-QtdhW
- ↑ http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/2009/myb3-sum-2009-middle-east.pdf
- ↑ http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/2010/myb3-2010-in.pdf
- ↑ http://www.jersey.uoregon.edu/~mstrick/GeoTours/TectonicBkgrnd.html
- ↑ http://www.indiana.edu/~geol116/week6/regional.swf
1. http://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
2. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
3. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html
4. http://www.weatherbase.com/search/search.php3?query=new+delhi+india+snow
7. http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/pa/pa1303_full.html
8. http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/melnd.htm
9. http://www.kilimanjaro.cc/elbrus2.htm
10.http://www.gperfors.com/Middle%20East%20Vegetation.htm
11. http://www.findlocalweather.com/weather_maps/pressure_middle_east.html
13 and India Picture: https://encrypted-tbn1.google.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcToa0BF4NqH1KHDTom0Sjb2oPflgotqmC5hEpYwRTzHqY-QtdhW
15. http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/2010/myb3-2010-in.pdf
16. http://www.jersey.uoregon.edu/~mstrick/GeoTours/TectonicBkgrnd.html