Photons
The Photon is a boson, a force carrier particle. It is the force carrier of electromagnetism. Photons of different energies are responsible for the entire spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. However, unlike other elementary particles it has zero rest mass. Which makes sense because that means that in a vacuum it travels at the speed of light. It has polarization and has momentum. It also has a spin of 1.
Discovery
1900 Planck tried to explain the black body emission spectrum by saying that the light energy is irradiated proportionally to the electromagnetic wave frequency: hv
1905 Einstein said that the photoeffect depended not on the intensity but the frequency and related that to energy: E=hv
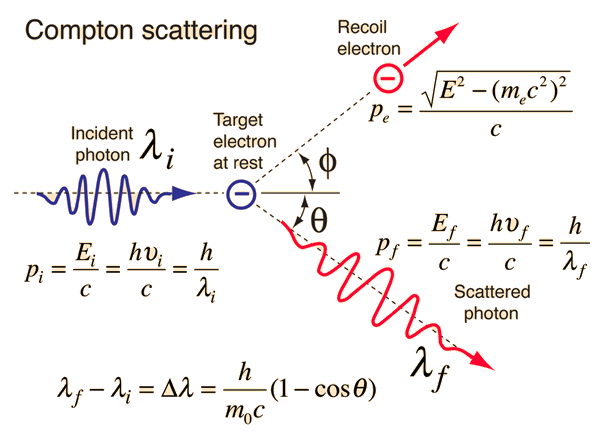
1923 Compton got it right.
Arthur Compton shot X-rays at electrons with the expectation that the electrons would re-emit waves in all directions at the same frequency as the X-rays. However, it did not happen that way. As the angle changed the wavelength and energy also changed. The data fit perfectly if he treated light as a collection of particles that obeyed the laws of momentum and described them by the following equations.
E=hv
p=hv/c
and m=0
They all promptly received Nobel Prizes
Application
Today the photon is being used to measure molecular distances. Research is also being poured in to the use of photons in quantum computers. If information can be carried by the photon then the processing power and speed of computers would increase exponentially.
Reference
http://lofi.forum.physorg.com/Changing-the-Frequency-of-Light_5770.html http://www.phys.ufl.edu/~korytov/ParticlePhysics/note_A02_e_p_photon_n.pdf http://particleadventure.org/frameless/electromagnetism.html