Difference between revisions of "India/Middle East 8"
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
<ref>http://www.weatherbase.com/search/search.php3?query=new+delhi+india+snow</ref> | <ref>http://www.weatherbase.com/search/search.php3?query=new+delhi+india+snow</ref> | ||
=='''Average Monthly Precipitation India'''== | =='''Average Monthly Precipitation India'''== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Temperature''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jan''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Feb''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Mar''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Apr''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''May''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jun''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jul''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Aug''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Sep''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Oct''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Nov''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Dec''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Annual''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Avg. Temperature ||48 ||54 ||62 ||72 ||82 ||90 ||94 ||92 ||86 ||76 ||61 ||52 ||72 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Avg. Max Temperature ||58 ||64 ||73 ||84 ||96 ||105 ||110 ||108 ||103 ||91 ||74 ||62 ||86 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Min: ann: 59 38 43 50 59 68 74 78 75 70 60 47 42 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Avg. Min Temperature ||38 ||43 ||50 ||59 ||68 ||74 ||78 ||75 ||70 ||60 ||47 ||42 ||59 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===''Average Precipitation''=== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Precipitation''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jan''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Feb''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Mar''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Apr''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''May''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jun''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Jul''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Aug''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Sep''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Oct''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Nov''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Dec''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Annual''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Precipitation (inches) || 1.1 ||1.1 ||1.1 ||0.7 ||0.3 ||--- ||--- ||--- ||--- ||0.1 ||0.8 ||1 ||6.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Days with Precipitation ||11.0 ||9.0 ||9.0 ||7.0 ||8.0 ||9.0 ||9.0 ||9.0 ||9.0 ||8.0 ||8.0 ||9.0 ||106 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
Monsoon are a large contributor to India's weather. The summer monsoons roar onto the subcontinent from the southwest. The winds carry moisture from the Indian Ocean and bring heavy rains from June to September. The torrential rainstorms often cause violent landslides. Entire villages have been swept away during monsoon rains. Despite the potential for destruction, the summer monsoons are welcomed in India. Farmers depend on the rains to irrigate their land. Additionally, a great deal of India’s electricity is generated by water power provided by the monsoon rains. The southwest summer monsoon is attracted to India by a low pressure area that's caused by the extreme heat of the Thar Desert and adjoining areas, during summer. Moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean come to fill up the void, but because they can't pass through the Himalaya region, they're forced to rise. The gain in altitude of the clouds results in a drop in temperature, bringing about rain. | Monsoon are a large contributor to India's weather. The summer monsoons roar onto the subcontinent from the southwest. The winds carry moisture from the Indian Ocean and bring heavy rains from June to September. The torrential rainstorms often cause violent landslides. Entire villages have been swept away during monsoon rains. Despite the potential for destruction, the summer monsoons are welcomed in India. Farmers depend on the rains to irrigate their land. Additionally, a great deal of India’s electricity is generated by water power provided by the monsoon rains. The southwest summer monsoon is attracted to India by a low pressure area that's caused by the extreme heat of the Thar Desert and adjoining areas, during summer. Moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean come to fill up the void, but because they can't pass through the Himalaya region, they're forced to rise. The gain in altitude of the clouds results in a drop in temperature, bringing about rain. | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 4 December 2011
Contents
- 1 India and the Middle East
- 2 Major Seas-Middle East :
- 3 The Latitude and Longitude Regions-Middle East :
- 4 Elevation Range-Middle East
- 5 Large Bodies of Water-Middle East
- 6 Topographic Features-Middle Est
- 7 Bordering Oceans-Middle East
- 8 Major Bodies of Water-India
- 9 Highest and Lowest Point-India
- 10 Latitude and Longitude Coordinates-India
- 11 Topographic features-India
- 12 Bordering Oceans-India
- 13 Average Monthly Temperature India
- 14 Average Monthly Precipitation India
- 15 Middle East Regions
India and the Middle East
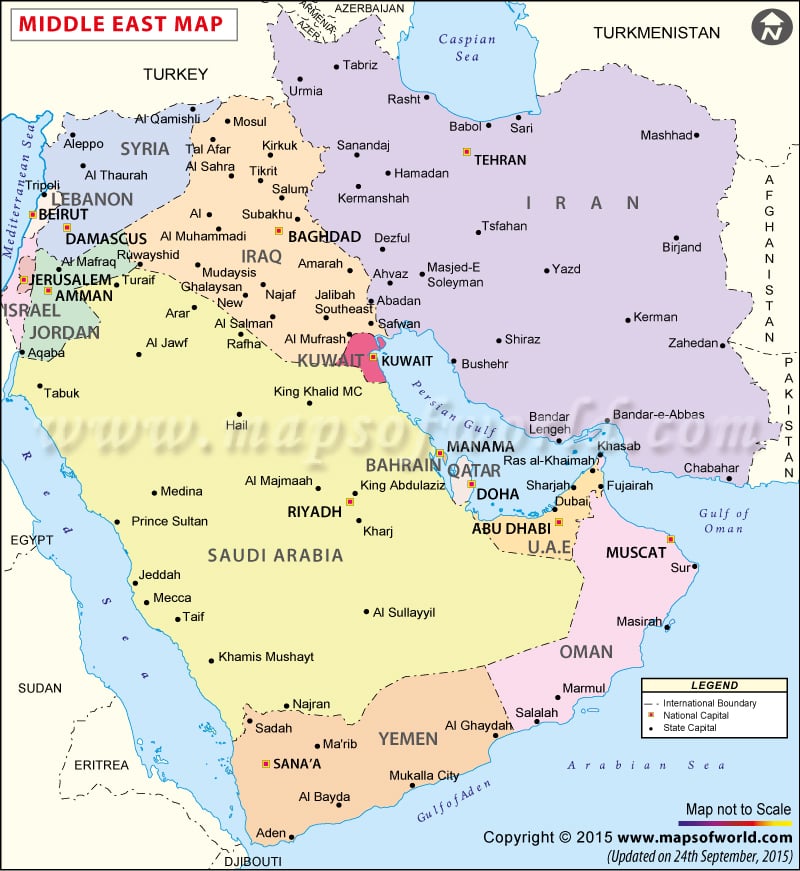
Countries-Middle East: Egypt Iran Turkey Sudan Algeria Morocco Iraq Saudi Arabia Yemen Syria Israel Libya Jordan United Arab Emirates Lebanon Palestinian territories Kuwait Oman Qatar Bahrain
Major Seas-Middle East :
Red Sea Gulf of Aqaba Arabian Gulf <refernces/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html>
The Latitude and Longitude Regions-Middle East :
Latitude: 30 (N) Longitude: 45 (E)
Elevation Range-Middle East
Lowest: The Dead Sea on the boarder of Israel and Jordan in the Middle its height is 1,388 ft below sea level Highest: Pik Samani at 24,590 ft
Large Bodies of Water-Middle East
Dead Sea Mediterranean Sea Black Sea Red Sea Caspian Sea Arabian Sea
Topographic Features-Middle Est
Rub al Khali dessert Caucasus Mts Elbruz Mts Zagros Mts
Bordering Oceans-Middle East
Indian Ocean
Major Bodies of Water-India
Ganges River
Highest and Lowest Point-India
The lowest point in India is the Indian Ocean at 0 feet above sea level. The highest point in India is Kangchenjunga at 20,209 ft above sea level.[[1]]
Latitude and Longitude Coordinates-India
20 00 N, 77 00 E [[2]]
Topographic features-India
Deccan Plateau [[3]]
Bordering Oceans-India
Bay of Bengal Arabian Sea Laccadive Sea [[4]]
Average Monthly Temperature India
| New Delhi,India Temperature in Farenheit | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual | ||
| Avg. Temperature F | 58 | 63 | 73 | 84 | 91 | 92 | 87 | 86 | 85 | 79 | 69 | 60 | 77 | ||
| Avg. Max Temperature | 68 | 73 | 83 | 95 | 101 | 101 | 93 | 91 | 92 | 90 | 81 | 71 | 87 | ||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 48 | 53 | 62 | 72 | 80 | 83 | 81 | 80 | 78 | 68 | 57 | 49 | 68 | ||
Average Monthly Precipitation India
| Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Temperature | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Avg. Temperature | 48 | 54 | 62 | 72 | 82 | 90 | 94 | 92 | 86 | 76 | 61 | 52 | 72 |
| Avg. Max Temperature | 58 | 64 | 73 | 84 | 96 | 105 | 110 | 108 | 103 | 91 | 74 | 62 | 86 |
| Min: ann: 59 38 43 50 59 68 74 78 75 70 60 47 42 | |||||||||||||
| Avg. Min Temperature | 38 | 43 | 50 | 59 | 68 | 74 | 78 | 75 | 70 | 60 | 47 | 42 | 59 |
Average Precipitation
| Baghdad, Iraq (BWk) Average Precipitation | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| Precipitation (inches) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1 | 6.1 |
| Days with Precipitation | 11.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 106 |
Monsoon are a large contributor to India's weather. The summer monsoons roar onto the subcontinent from the southwest. The winds carry moisture from the Indian Ocean and bring heavy rains from June to September. The torrential rainstorms often cause violent landslides. Entire villages have been swept away during monsoon rains. Despite the potential for destruction, the summer monsoons are welcomed in India. Farmers depend on the rains to irrigate their land. Additionally, a great deal of India’s electricity is generated by water power provided by the monsoon rains. The southwest summer monsoon is attracted to India by a low pressure area that's caused by the extreme heat of the Thar Desert and adjoining areas, during summer. Moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean come to fill up the void, but because they can't pass through the Himalaya region, they're forced to rise. The gain in altitude of the clouds results in a drop in temperature, bringing about rain.
When the southwest monsoon reaches India, it splits into two parts around the mountainous region of the Western Ghats in south-central India. One part moves northwards over the Arabian Sea and up the coastal side of the Western Ghats. The other flows over the Bay of Bengal, up through Assam, and hits the Eastern Himalaya range.
Middle East Regions
According to the Koppen Classification System, the Middle East is BWh and BSk
The Middle East also experiences monsoons, without the rain. The Middle Eastern climate is very dry and hot.
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found