Difference between revisions of "Earth Science 7-Central America2"
(→Climate Zones) |
m (→Climate Zones) |
||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
[[http://geography.about.com/library/faq/blqzantilles.html]][[http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/camerica.htm]] | [[http://geography.about.com/library/faq/blqzantilles.html]][[http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/camerica.htm]] | ||
| − | The climate in Central America is equatorial monsoonal, and equatorial winter dry. Central America is surrounded by water on either side of it, some of the countries are islands so you can expect proximity to water to control and affect its weather. Central America is above sea level, keeping it cooler than if it was at sea level. There are many volcanoes and mountains that contribute to the climate change, by blocking strong winds or other precipitation. Central America is fairly close to the equator causing it to have a warm climate. Warm ocean currents (S. Equatorial) affect the eastern side of Central America, while the western side is affected by a cold California Current. Wind currents affect the western side of Central America with the North Equatorial Current, and the eastern side is affected by the Gulf Stream Current. The small islands affect the climate zones because they are tropical and their warm humid air moves into the mainland affecting the climate zones. | + | The climate in Central America is equatorial monsoonal, and equatorial winter dry. Central America is surrounded by water on either side of it, some of the countries are islands so you can expect proximity to water to control and affect its weather. Central America is above sea level, keeping it cooler than if it was at sea level. There are many volcanoes and mountains that contribute to the climate change, by blocking strong winds or other precipitation. Central America is fairly close to the equator causing it to have a warm climate. Warm ocean currents (S. Equatorial) affect the eastern side of Central America, while the western side is affected by a cold California Current. Wind currents affect the western side of Central America with the North Equatorial Current, and the eastern side is affected by the Gulf Stream Current. The small islands affect the climate zones because they are tropical and their warm humid air moves into the mainland affecting the climate zones. |
| + | |||
| + | The Koepper Chart was very helpful with this study of the clinmate zones. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 18 November 2011
Earth Science 7-Global Regions Index
[[1]]
Contents
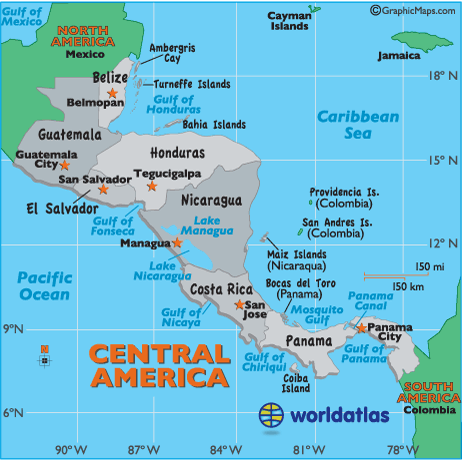
Countries in Central America
[[2]]
1. Belize (Capital, Belmopan)
2. Guatemala (Capital, Guatemala City)
3. Honduras (Capital, Tegucigalpa)
4. Nicaragua (Capital, Managua)
5. Costa Rica (Capital, San Jose)
6. Panama (Capital, Panama City)
7. El Salvador (Capital, San Salvador)
8. Cuba (Capital, La Havana)
9. Puerto Rico (Capital, San Juan)
10. The Lesser of Antilles
Islands in Central America
[[3]]
1. Turneffe Islands
2. Isla de la Bahia Islands (Bay Islands)
3. Providencia Islands
4. San Andres Islands
5. Maiz Islands
6. Coiba Island
7. Cayos Cocinos (Hog Islands)
8. Swan Islands
9. Ometepe Island
10. Pearl Islands
11. Taboga Islands
12. Cebaco Islands
13. Coiba Islands
14. Barbados
15. Haiti (Capital, Port-au-Prince)
16. Dominican Republic (Capital, Santo Domingo)
17. Jamaica
Main Bodies of Water in and Surrounding Central America
[[4]]
1. Gulf of Honduras
2. Caribbean Sea
3. Mosquito Gulf
4. Panama Canal
5. Gulf of Panama
6. Gulf of Chiriqul
7. Gulf of Nicaya
8. Pacific Ocean
9. Gulf of Fonseca
10. Lake Managua
11. Lake Nicaragua
12. Lake Izabal
13. Motagua River
Latitude and Longitude
General Knowledge
(17°-5°N) (91°-15°W)
Elevation Range
[[5]]
The highest point in Central America is the Tajamulco Volcano, which is located in the country of Guatemala. It is 13,845 feet (4,220 meters) above sea level.
The lowest point in Central America is the Carribean Sea, which is 0 feet (0 meters) above sea level.
Topographic Features
[[6]]
Sierra Madre de Chiapas (Volcano Range)
Cordillera Isabella (Volcano Range)
Cordillera de Talamanca (Volcano Range)
Rainforests
Barrier Reef
The Blue Hole (An opening to a former Ice Age cave and popular dive spot)
Sierra Madre Mountains
The Central Highlands
Carribean Lowlands
Central Mountains
Bocas del Torro (Collection of Islands)
San Blas Archipelagos (Collection of Islands)
Darian Gap (Jungle)
Climate Zones
The climate in Central America is equatorial monsoonal, and equatorial winter dry. Central America is surrounded by water on either side of it, some of the countries are islands so you can expect proximity to water to control and affect its weather. Central America is above sea level, keeping it cooler than if it was at sea level. There are many volcanoes and mountains that contribute to the climate change, by blocking strong winds or other precipitation. Central America is fairly close to the equator causing it to have a warm climate. Warm ocean currents (S. Equatorial) affect the eastern side of Central America, while the western side is affected by a cold California Current. Wind currents affect the western side of Central America with the North Equatorial Current, and the eastern side is affected by the Gulf Stream Current. The small islands affect the climate zones because they are tropical and their warm humid air moves into the mainland affecting the climate zones.
The Koepper Chart was very helpful with this study of the clinmate zones.
References
[[9]]
General knowledge
[[10]]
[[11]]