History 8 China Manual
Return to History 8. Be sure to sign your entry.
Role of the environment in China
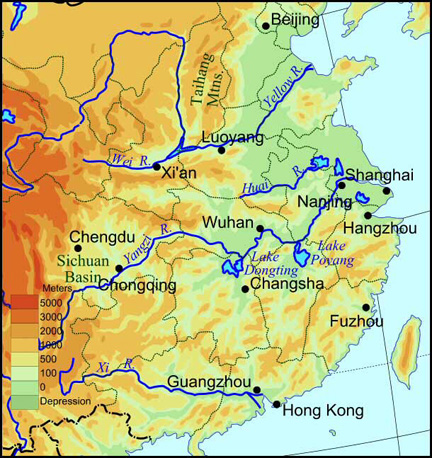
China's territory is characterized by its geographical diversity. Most of the country, to be more specific, two- thirds of it, is filled with mountains and plateaus. China has extremely dry land in the north and west, and in the east and southeast it is rainy and and hot with tropical monsoons. Most of the country still lies in the moderate zone and has four seasons. There are two major rivers that run through China Proper: the Yellow River, in the north and the Yangtzi, in the south. In the north it is covered in new silt carried down by the Yellow River, so it is well suited for agriculture. Their main crops vary from wheat, corn, sorghum, millet, and soybeans. Now-a-days, rice has become more and more popular to grow. This part of China is mostly flat. South China is hillier, warmer, and more humid than North China. Outside of China Proper there is a huge area to the north and west. In the Northeast of Outer China it is a combination of prairie, mountain, desert, and is a great for raising sheep. In Northwestern China there is extremely dry weather which is great for growing fruits like melons and grapes. The Tibetan Plateau, in Southwest China, is composed of VERY tall mountains and massive highlands. it is about 13000 to 15000 feet above sea level. China has been hit by many earthquakes.
PRA
Chinese concept of civilization
Mandate of heaven *Michael Huang's